Robotic Inspection and Characterization of Subsurface Defects on Concrete Structures Using Impact Sounding
Paper and Code
Aug 12, 2022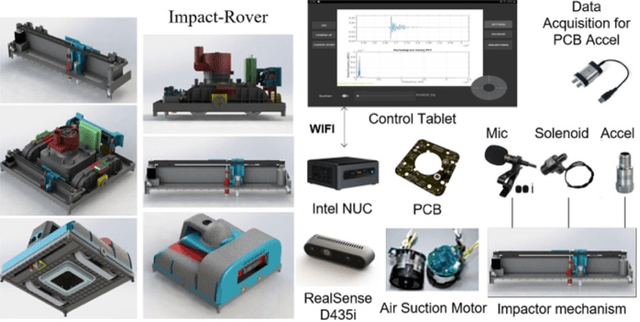
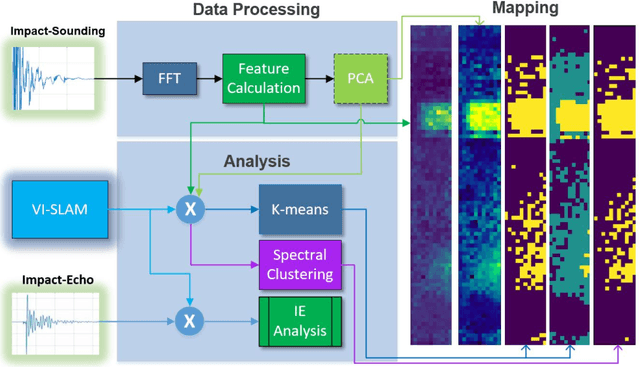
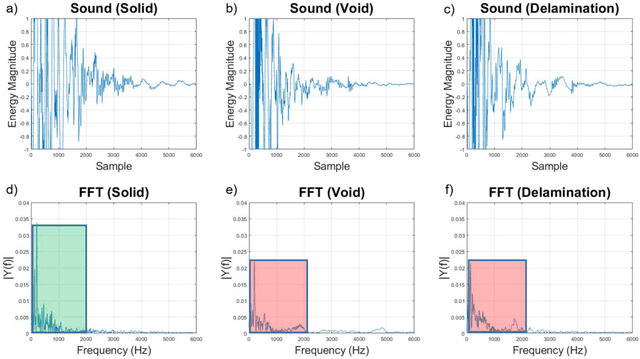
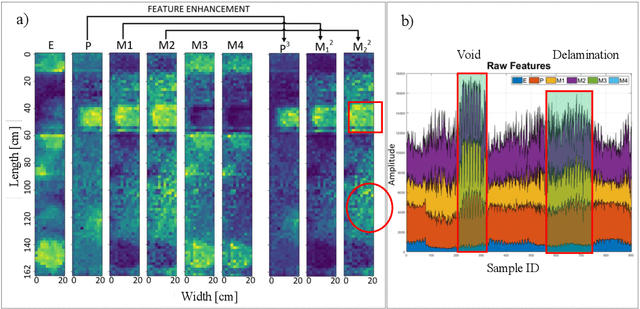
Impact-sounding (IS) and impact-echo (IE) are well-developed non-destructive evaluation (NDE) methods that are widely used for inspections of concrete structures to ensure the safety and sustainability. However, it is a tedious work to collect IS and IE data along grid lines covering a large target area for characterization of subsurface defects. On the other hand, data processing is very complicated that requires domain experts to interpret the results. To address the above problems, we present a novel robotic inspection system named as Impact-Rover to automate the data collection process and introduce data analytics software to visualize the inspection result allowing regular non-professional people to understand. The system consists of three modules: 1) a robotic platform with vertical mobility to collect IS and IE data in hard-to-reach locations, 2) vision-based positioning module that fuses the RGB-D camera, IMU and wheel encoder to estimate the 6-DOF pose of the robot, 3) a data analytics software module for processing the IS data to generate defect maps. The Impact-Rover hosts both IE and IS devices on a sliding mechanism and can perform move-stop-sample operations to collect multiple IS and IE data at adjustable spacing. The robot takes samples much faster than the manual data collection method because it automatically takes the multiple measurements along a straight line and records the locations. This paper focuses on reporting experimental results on IS. We calculate features and use unsupervised learning methods for analyzing the data. By combining the pose generated by our vision-based localization module and the position of the head of the sliding mechanism we can generate maps of possible defects. The results on concrete slabs demonstrate that our impact-sounding system can effectively reveal shallow defects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge