Risk-Averse Reinforcement Learning via Dynamic Time-Consistent Risk Measures
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2023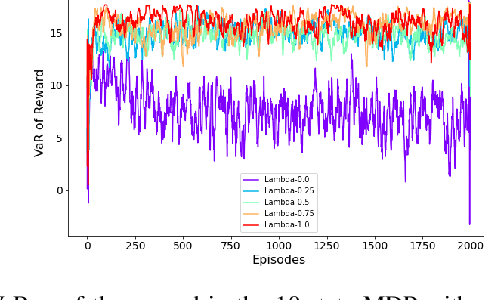
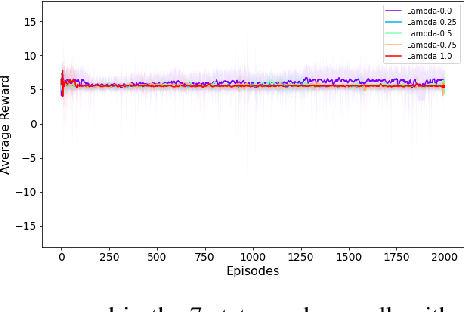
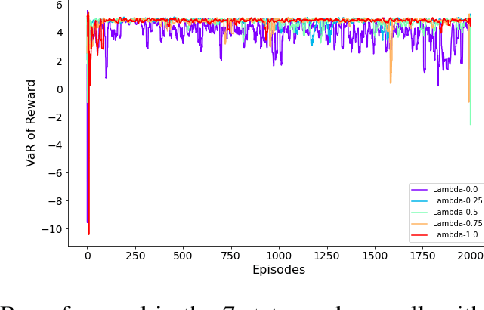
Traditional reinforcement learning (RL) aims to maximize the expected total reward, while the risk of uncertain outcomes needs to be controlled to ensure reliable performance in a risk-averse setting. In this paper, we consider the problem of maximizing dynamic risk of a sequence of rewards in infinite-horizon Markov Decision Processes (MDPs). We adapt the Expected Conditional Risk Measures (ECRMs) to the infinite-horizon risk-averse MDP and prove its time consistency. Using a convex combination of expectation and conditional value-at-risk (CVaR) as a special one-step conditional risk measure, we reformulate the risk-averse MDP as a risk-neutral counterpart with augmented action space and manipulation on the immediate rewards. We further prove that the related Bellman operator is a contraction mapping, which guarantees the convergence of any value-based RL algorithms. Accordingly, we develop a risk-averse deep Q-learning framework, and our numerical studies based on two simple MDPs show that the risk-averse setting can reduce the variance and enhance robustness of the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge