RIS-Augmented Millimeter-Wave MIMO Systems for Passive Drone Detection
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2024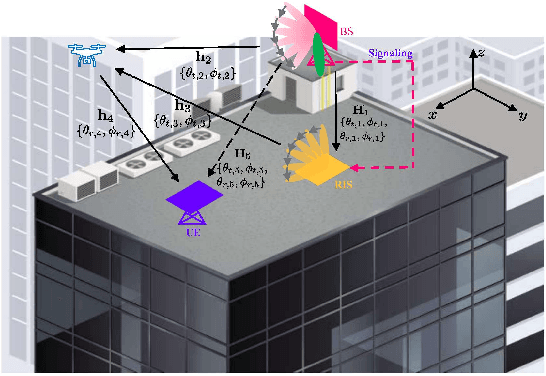
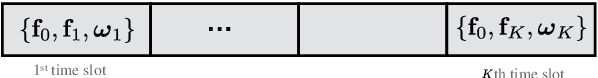
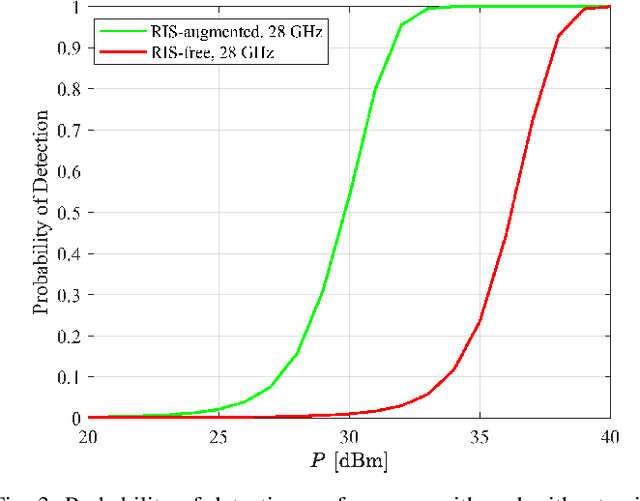
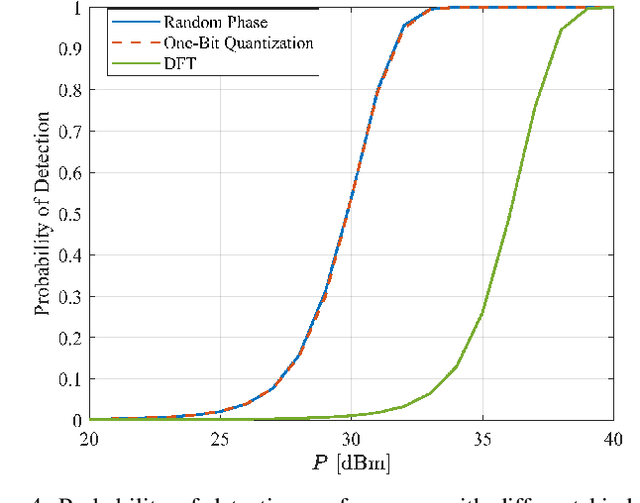
In the past decade, the number of amateur drones is increasing, and this trend is expected to continue in the future. The security issues brought by abuse and misconduct of drones become more and more severe and may incur a negative impact to the society. In this paper, we leverage existing cellular multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) base station (BS) infrastructure, operating at millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency bands, for drone detection in a device-free manner with the aid of one reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), deployed in the proximity of the BS. We theoretically examine the feasibility of drone detection with the aid of the generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) and validate via simulations that, the optimized deployment of an RIS can bring added benefits compared to RIS-free systems. In addition, the effect of RIS training beams, training overhead, and radar cross section, is investigated in order to offer theoretical design guidance for the proposed cellular RIS-based passive drone detection system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge