Revisiting the Initial Steps in Adaptive Gradient Descent Optimization
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2024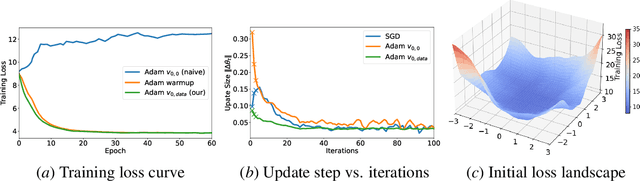

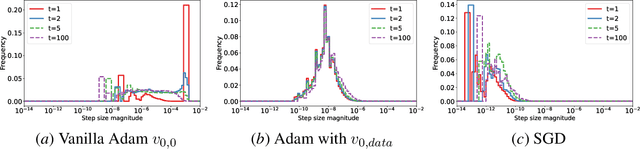
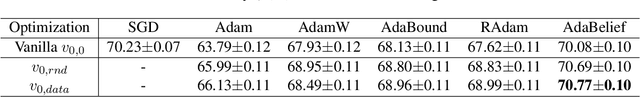
Adaptive gradient optimization methods, such as Adam, are prevalent in training deep neural networks across diverse machine learning tasks due to their ability to achieve faster convergence. However, these methods often suffer from suboptimal generalization compared to stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and exhibit instability, particularly when training Transformer models. In this work, we show the standard initialization of the second-order moment estimation ($v_0 =0$) as a significant factor contributing to these limitations. We introduce simple yet effective solutions: initializing the second-order moment estimation with non-zero values, using either data-driven or random initialization strategies. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our approach not only stabilizes convergence but also enhances the final performance of adaptive gradient optimizers. Furthermore, by adopting the proposed initialization strategies, Adam achieves performance comparable to many recently proposed variants of adaptive gradient optimization methods, highlighting the practical impact of this straightforward modification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge