Retrofitting Distributional Embeddings to Knowledge Graphs with Functional Relations
Paper and Code
Jun 16, 2018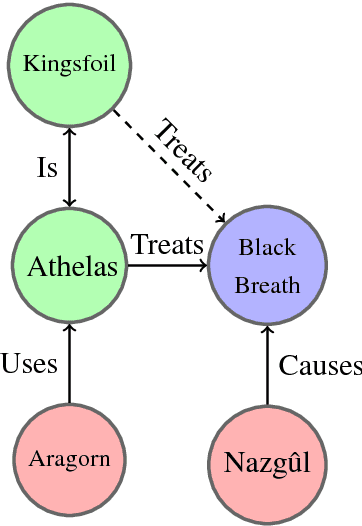
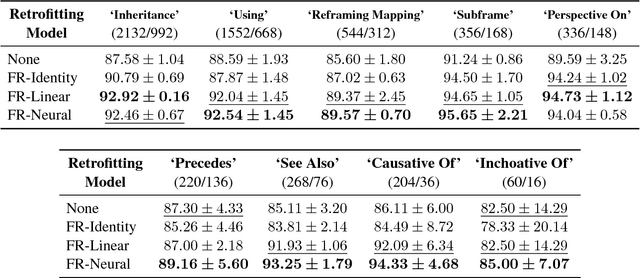
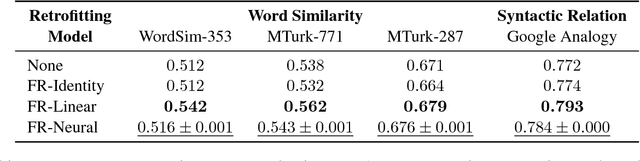
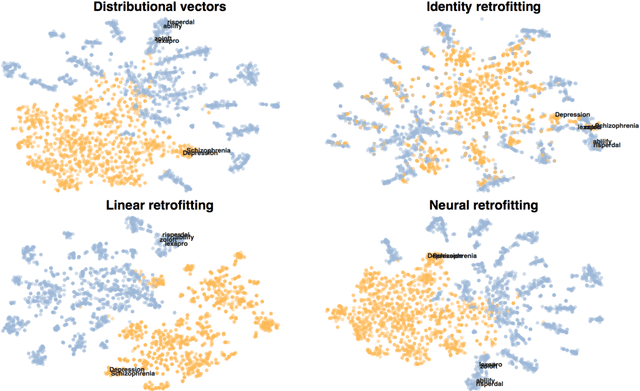
Knowledge graphs are a versatile framework to encode richly structured data relationships, but it can be challenging to combine these graphs with unstructured data. Methods for retrofitting pre-trained entity representations to the structure of a knowledge graph typically assume that entities are embedded in a connected space and that relations imply similarity. However, useful knowledge graphs often contain diverse entities and relations (with potentially disjoint underlying corpora) which do not accord with these assumptions. To overcome these limitations, we present Functional Retrofitting, a framework that generalizes current retrofitting methods by explicitly modeling pairwise relations. Our framework can directly incorporate a variety of pairwise penalty functions previously developed for knowledge graph completion. Further, it allows users to encode, learn, and extract information about relation semantics. We present both linear and neural instantiations of the framework. Functional Retrofitting significantly outperforms existing retrofitting methods on complex knowledge graphs and loses no accuracy on simpler graphs (in which relations do imply similarity). Finally, we demonstrate the utility of the framework by predicting new drug--disease treatment pairs in a large, complex health knowledge graph.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge