ReLGAN: Generalization of Consistency for GAN with Disjoint Constraints and Relative Learning of Generative Processes for Multiple Transformation Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2020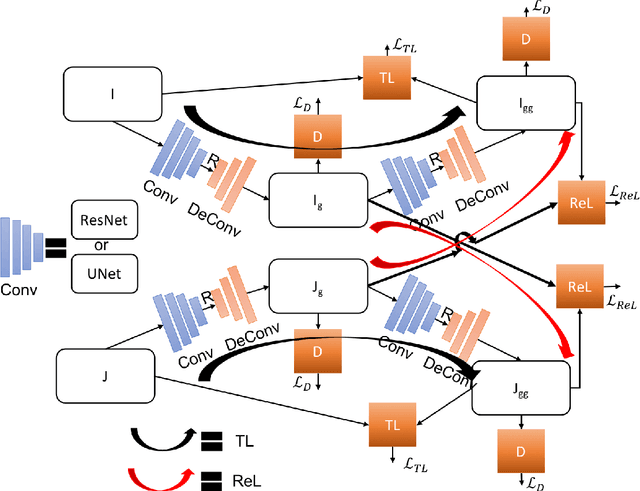
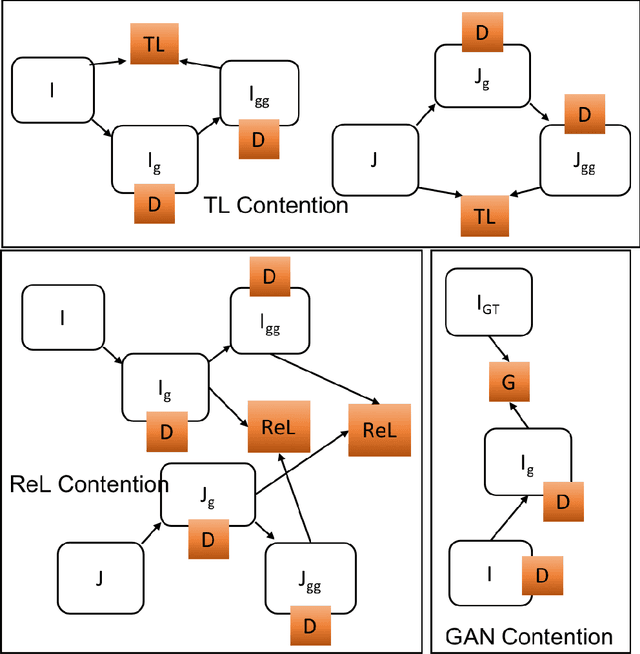
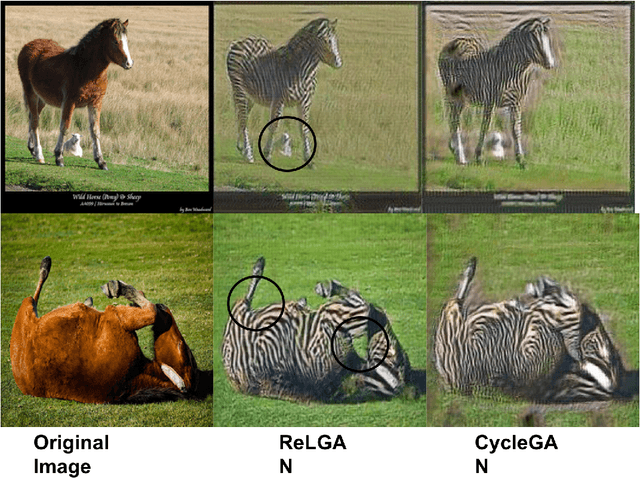
Image to image transformation has gained popularity from different research communities due to its enormous impact on different applications, including medical. In this work, we have introduced a generalized scheme for consistency for GAN architectures with two new concepts of Transformation Learning (TL) and Relative Learning (ReL) for enhanced learning image transformations. Consistency for GAN architectures suffered from inadequate constraints and failed to learn multiple and multi-modal transformations, which is inevitable for many medical applications. The main drawback is that it focused on creating an intermediate and workable hybrid, which is not permissible for the medical applications which focus on minute details. Another drawback is the weak interrelation between the two learning phases and TL and ReL have introduced improved coordination among them. We have demonstrated the capability of the novel network framework on public datasets. We emphasized that our novel architecture produced an improved neural image transformation version for the image, which is more acceptable to the medical community. Experiments and results demonstrated the effectiveness of our framework with enhancement compared to the previous works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge