ReconROS Executor: Event-Driven Programming of FPGA-accelerated ROS 2 Applications
Paper and Code
Jan 19, 2022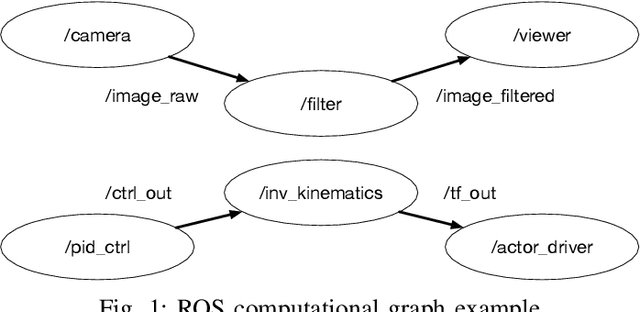
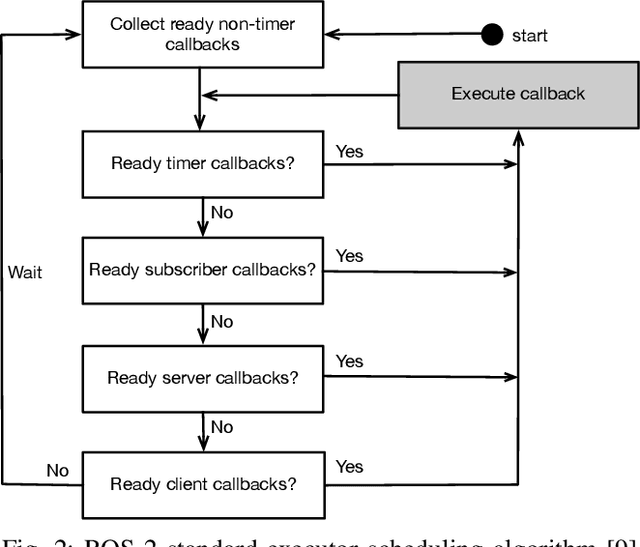
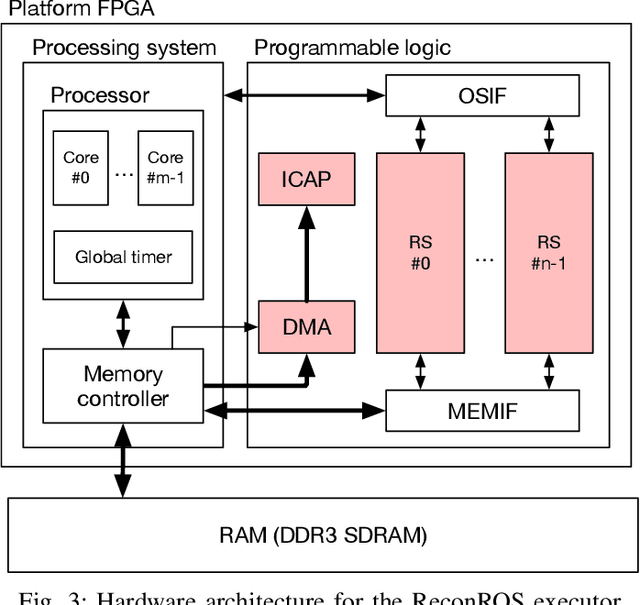
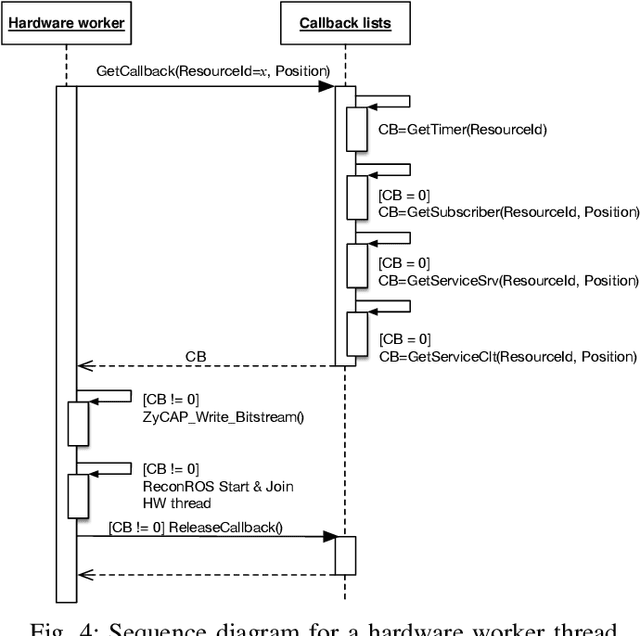
Many applications from the robotics domain can benefit from FPGA acceleration. A corresponding key question is how to integrate hardware accelerators into software-centric robotics programming environments. Recently, several approaches have demonstrated hardware acceleration for the robot operating system (ROS), the dominant programming environment in robotics. ROS is a middleware layer that features the composition of complex robotics applications as a set of nodes that communicate via mechanisms such as publish/subscribe, and distributes them over several compute platforms. In this paper, we present a novel approach for event-based programming of robotics applications that leverages ReconROS, a framework for flexibly mapping ROS 2 nodes to either software or reconfigurable hardware. The ReconROS executor schedules callbacks of ROS 2 nodes and utilizes a reconfigurable slot model and partial runtime reconfiguration to load hardware-based callbacks on demand. We describe the ReconROS executor approach, give design examples, and experimentally evaluate its functionality with examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge