Recognizing Instagram Filtered Images with Feature De-stylization
Paper and Code
Dec 30, 2019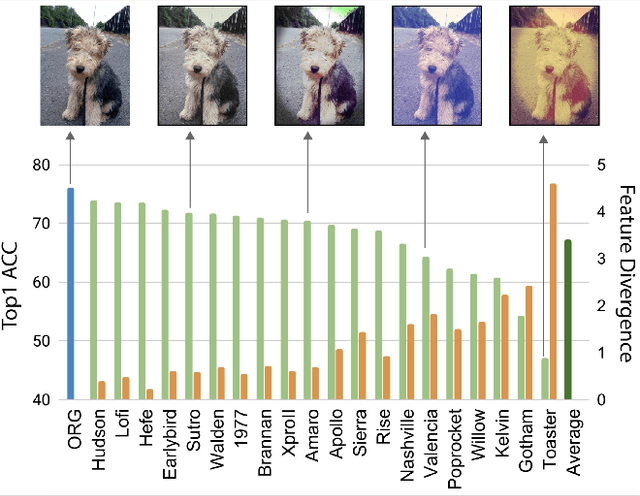


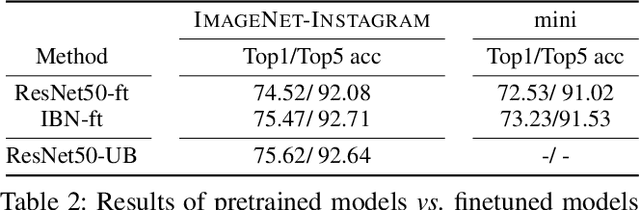
Deep neural networks have been shown to suffer from poor generalization when small perturbations are added (like Gaussian noise), yet little work has been done to evaluate their robustness to more natural image transformations like photo filters. This paper presents a study on how popular pretrained models are affected by commonly used Instagram filters. To this end, we introduce ImageNet-Instagram, a filtered version of ImageNet, where 20 popular Instagram filters are applied to each image in ImageNet. Our analysis suggests that simple structure preserving filters which only alter the global appearance of an image can lead to large differences in the convolutional feature space. To improve generalization, we introduce a lightweight de-stylization module that predicts parameters used for scaling and shifting feature maps to "undo" the changes incurred by filters, inverting the process of style transfer tasks. We further demonstrate the module can be readily plugged into modern CNN architectures together with skip connections. We conduct extensive studies on ImageNet-Instagram, and show quantitatively and qualitatively, that the proposed module, among other things, can effectively improve generalization by simply learning normalization parameters without retraining the entire network, thus recovering the alterations in the feature space caused by the filters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge