Real-Time Multiple Object Tracking - A Study on the Importance of Speed
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2017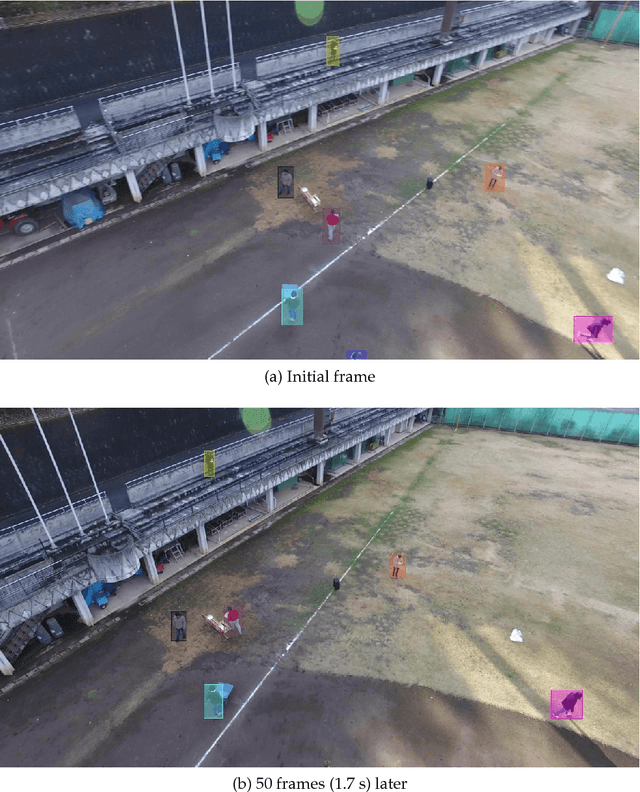

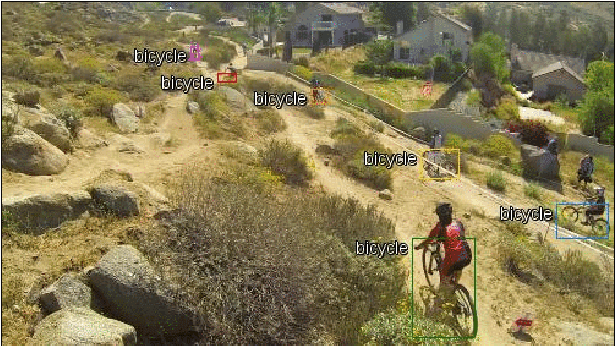
In this project, we implement a multiple object tracker, following the tracking-by-detection paradigm, as an extension of an existing method. It works by modelling the movement of objects by solving the filtering problem, and associating detections with predicted new locations in new frames using the Hungarian algorithm. Three different similarity measures are used, which use the location and shape of the bounding boxes. Compared to other trackers on the MOTChallenge leaderboard, our method, referred to as C++SORT, is the fastest non-anonymous submission, while also achieving decent score on other metrics. By running our model on the Okutama-Action dataset, sampled at different frame-rates, we show that the performance is greatly reduced when running the model - including detecting objects - in real-time. In most metrics, the score is reduced by 50%, but in certain cases as much as 90%. We argue that this indicates that other, slower methods could not be used for tracking in real-time, but that more research is required specifically on this.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge