Rate Splitting for 6G Optical Wireless Networks
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2023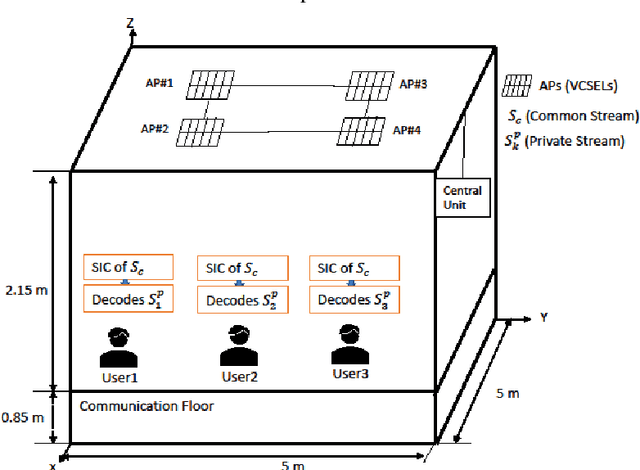
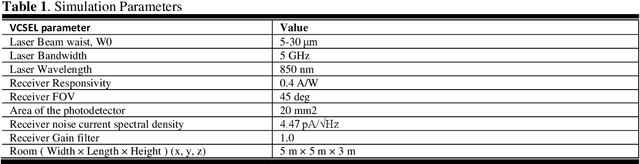
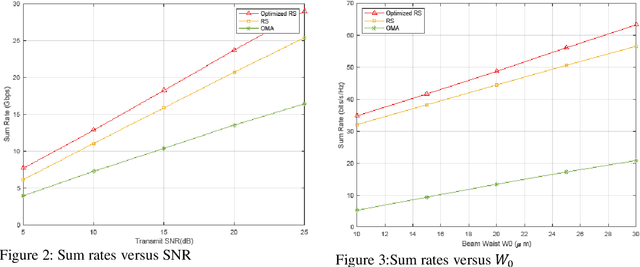
This paper evaluates the performance of rate splitting (RS), a robust interference management scheme, in an optical wireless communication (OWC) network that uses infrared lasers referred to as vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) as optical transmitters. In 6G OWC, providing high spectral and energy efficiency requires advanced multiple access schemes that can serve multiple users simultaneously in a non-orthogonal fashion. In this context, RS has the potential to manage multi-user interference at high data rates compared to orthogonal transmission schemes. Simulation results show the high performance of RS compared to baseline approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge