Query-oriented text summarization based on hypergraph transversals
Paper and Code
Feb 02, 2019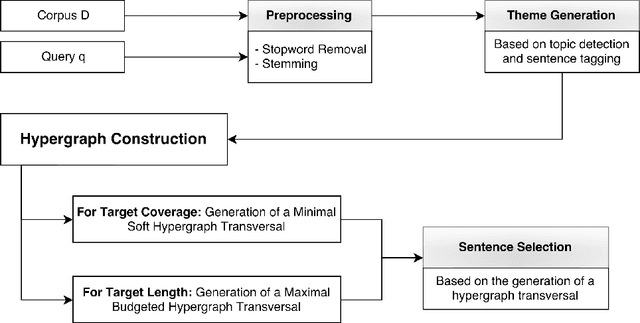
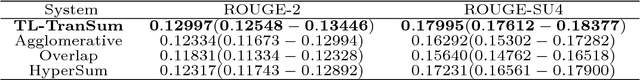
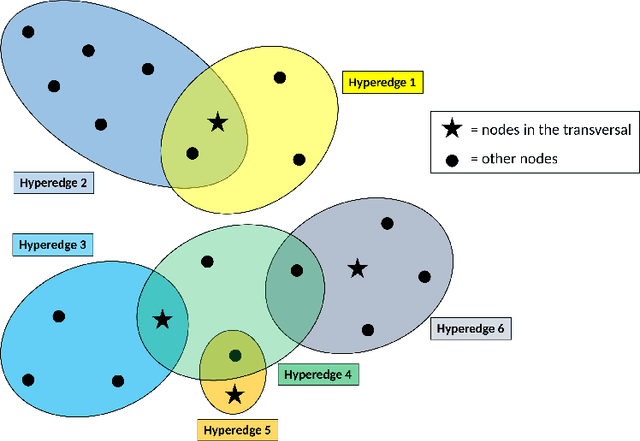
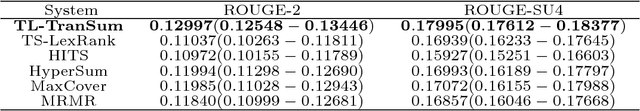
Existing graph- and hypergraph-based algorithms for document summarization represent the sentences of a corpus as the nodes of a graph or a hypergraph in which the edges represent relationships of lexical similarities between sentences. Each sentence of the corpus is then scored individually, using popular node ranking algorithms, and a summary is produced by extracting highly scored sentences. This approach fails to select a subset of jointly relevant sentences and it may produce redundant summaries that are missing important topics of the corpus. To alleviate this issue, a new hypergraph-based summarizer is proposed in this paper, in which each node is a sentence and each hyperedge is a theme, namely a group of sentences sharing a topic. Themes are weighted in terms of their prominence in the corpus and their relevance to a user-defined query. It is further shown that the problem of identifying a subset of sentences covering the relevant themes of the corpus is equivalent to that of finding a hypergraph transversal in our theme-based hypergraph. Two extensions of the notion of hypergraph transversal are proposed for the purpose of summarization, and polynomial time algorithms building on the theory of submodular functions are proposed for solving the associated discrete optimization problems. The worst-case time complexity of the proposed algorithms is squared in the number of terms, which makes it cheaper than the existing hypergraph-based methods. A thorough comparative analysis with related models on DUC benchmark datasets demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach, which outperforms existing graph- or hypergraph-based methods by at least 6% of ROUGE-SU4 score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge