Quasi Error-free Text Classification and Authorship Recognition in a large Corpus of English Literature based on a Novel Feature Set
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2020
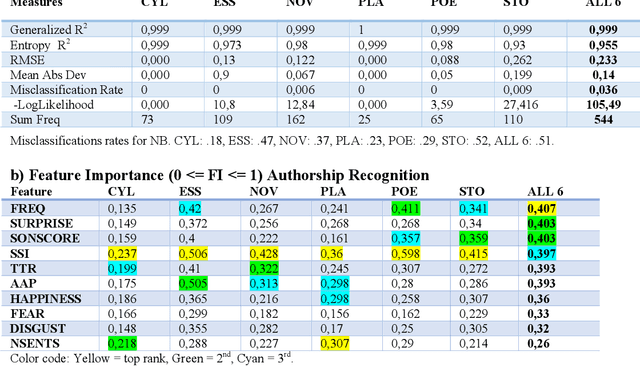
The Gutenberg Literary English Corpus (GLEC) provides a rich source of textual data for research in digital humanities, computational linguistics or neurocognitive poetics. However, so far only a small subcorpus, the Gutenberg English Poetry Corpus, has been submitted to quantitative text analyses providing predictions for scientific studies of literature. Here we show that in the entire GLEC quasi error-free text classification and authorship recognition is possible with a method using the same set of five style and five content features, computed via style and sentiment analysis, in both tasks. Our results identify two standard and two novel features (i.e., type-token ratio, frequency, sonority score, surprise) as most diagnostic in these tasks. By providing a simple tool applicable to both short poems and long novels generating quantitative predictions about features that co-determe the cognitive and affective processing of specific text categories or authors, our data pave the way for many future computational and empirical studies of literature or experiments in reading psychology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge