Quantum Algorithms for Data Representation and Analysis
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2021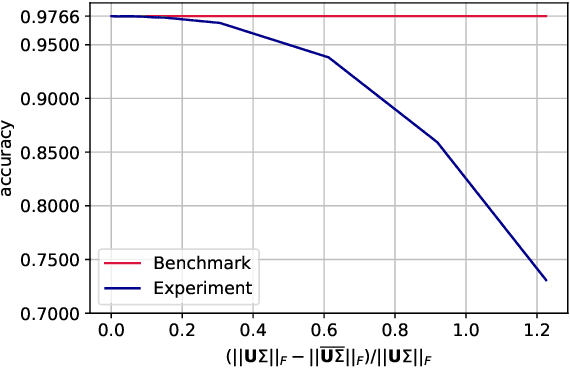
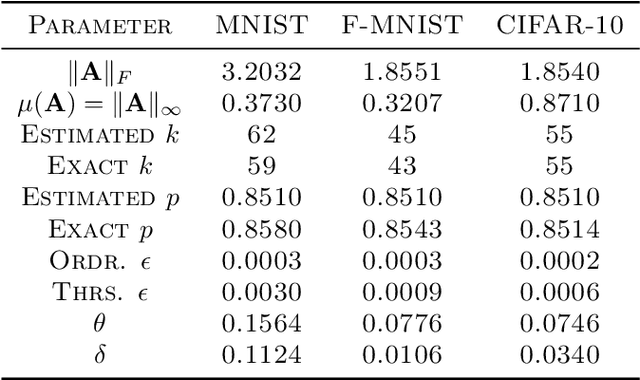
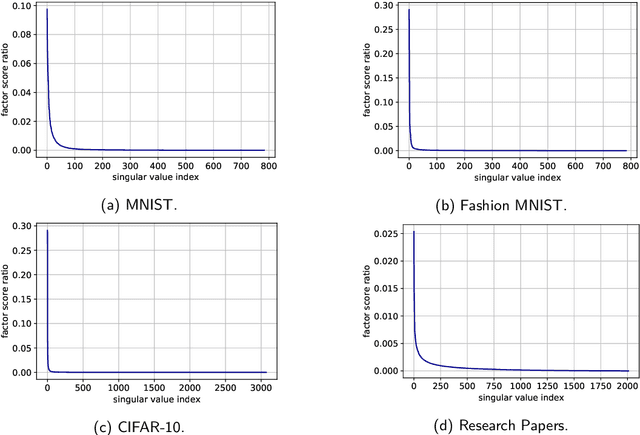
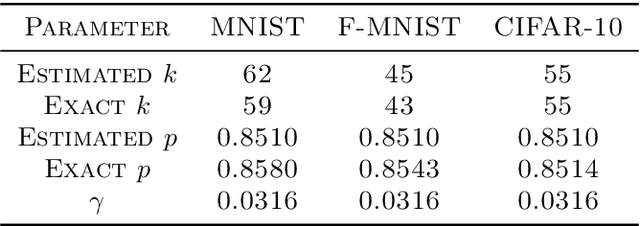
We narrow the gap between previous literature on quantum linear algebra and useful data analysis on a quantum computer, providing quantum procedures that speed-up the solution of eigenproblems for data representation in machine learning. The power and practical use of these subroutines is shown through new quantum algorithms, sublinear in the input matrix's size, for principal component analysis, correspondence analysis, and latent semantic analysis. We provide a theoretical analysis of the run-time and prove tight bounds on the randomized algorithms' error. We run experiments on multiple datasets, simulating PCA's dimensionality reduction for image classification with the novel routines. The results show that the run-time parameters that do not depend on the input's size are reasonable and that the error on the computed model is small, allowing for competitive classification performances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge