Quantitative Survey of the State of the Art in Sign Language Recognition
Paper and Code
Aug 29, 2020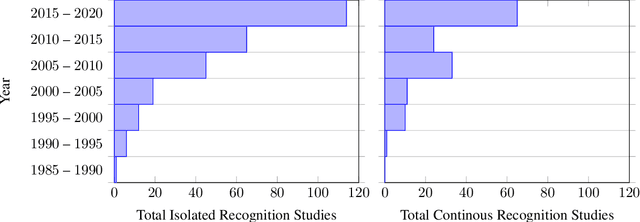
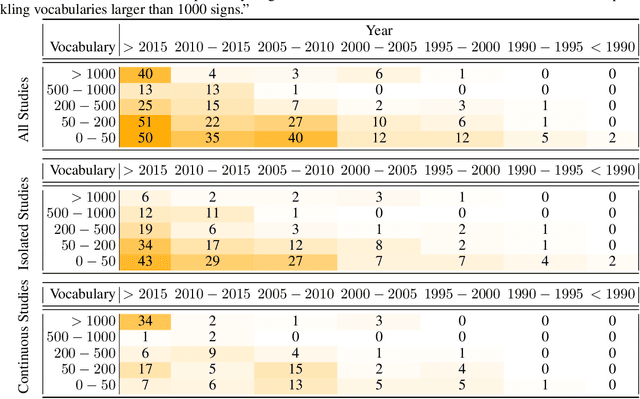
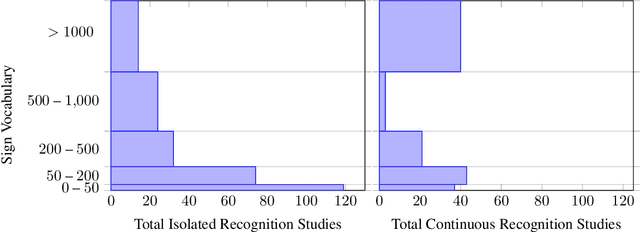
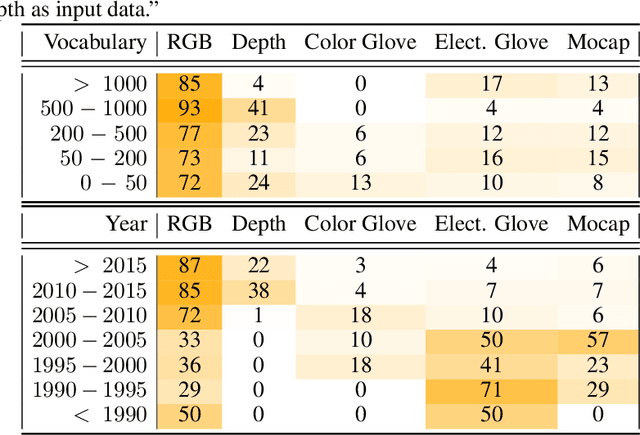
This work presents a meta study covering around 300 published sign language recognition papers with over 400 experimental results. It includes most papers between the start of the field in 1983 and 2020. Additionally, it covers a fine-grained analysis on over 25 studies that have compared their recognition approaches on RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather 2014, the standard benchmark task of the field. Research in the domain of sign language recognition has progressed significantly in the last decade, reaching a point where the task attracts much more attention than ever before. This study compiles the state of the art in a concise way to help advance the field and reveal open questions. Moreover, all of this meta study's source data is made public, easing future work with it and further expansion. The analyzed papers have been manually labeled with a set of categories. The data reveals many insights, such as, among others, shifts in the field from intrusive to non-intrusive capturing, from local to global features and the lack of non-manual parameters included in medium and larger vocabulary recognition systems. Surprisingly, RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather with a vocabulary of 1080 signs represents the only resource for large vocabulary continuous sign language recognition benchmarking world wide.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge