Quantifying the pathways to life using assembly spaces
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2019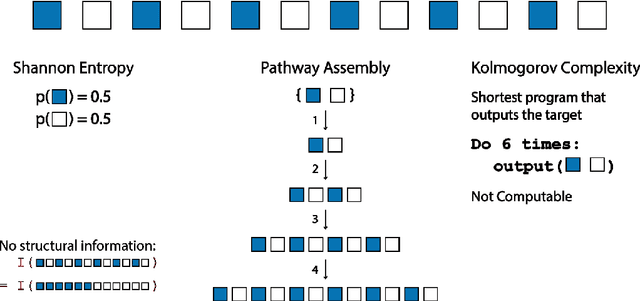
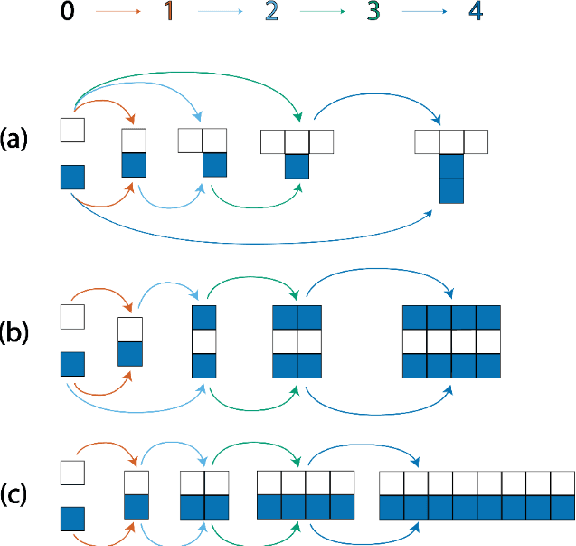
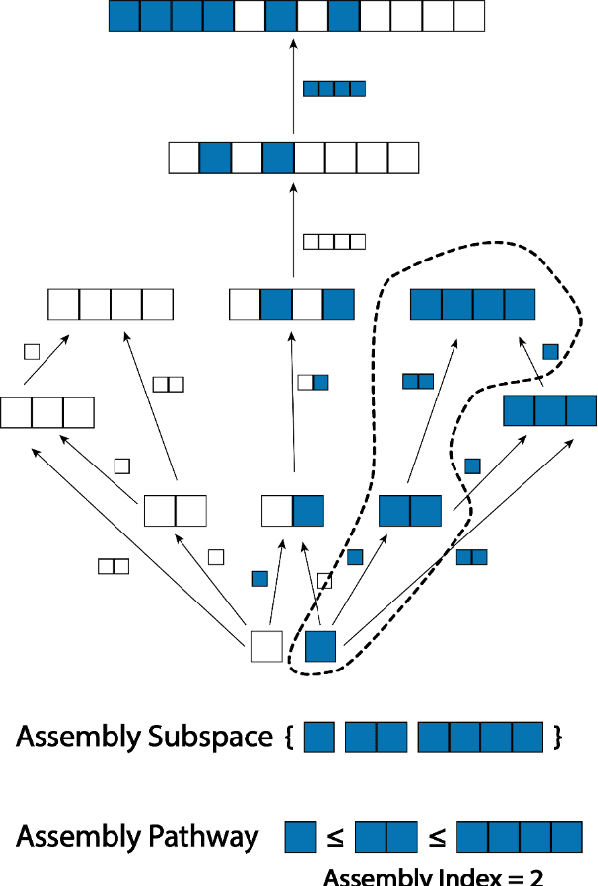
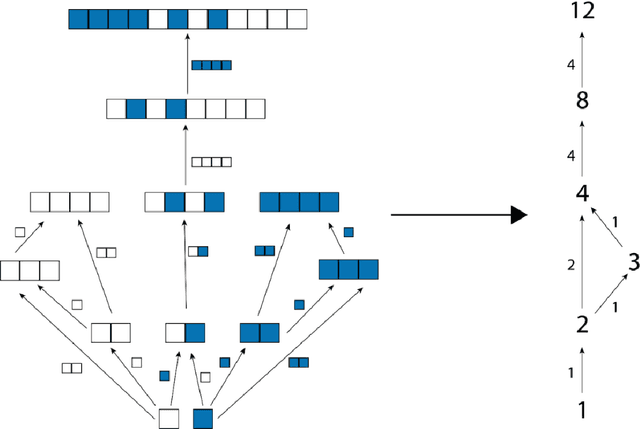
We have developed the concept of pathway assembly to explore the amount of extrinsic information required to build an object. To quantify this information in an agnostic way, we present a method to determine the amount of pathway assembly information contained within such an object by deconstructing the object into its irreducible parts, and then evaluating the minimum number of steps to reconstruct the object along any pathway. The mathematical formalisation of this approach uses an assembly space. By finding the minimal number of steps contained in the route by which the objects can be assembled within that space, we can compare how much information (I) is gained from knowing this pathway assembly index (PA) according to I_PA=log (|N|)/(|N_PA |) where, for an end product with PA=x, N is the set of objects possible that can be created from the same irreducible parts within x steps regardless of PA, and NPA is the subset of those objects with the precise pathway assembly index PA=x. Applying this formalism to objects formed in 1D, 2D and 3D space allows us to identify objects in the world or wider Universe that have high assembly numbers. We propose that objects with PA greater than a threshold are important because these are uniquely identifiable as those that must have been produced by biological or technological processes, rather than the assembly occurring via unbiased random processes alone. We think this approach is needed to help identify the new physical and chemical laws needed to understand what life is, by quantifying what life does.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge