Quantifying Memorization of Domain-Specific Pre-trained Language Models using Japanese Newspaper and Paywalls
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2024


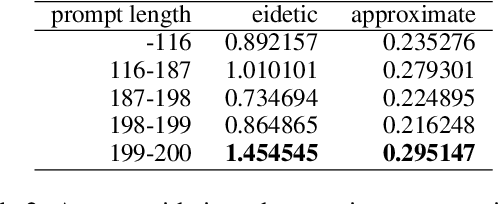
Dominant pre-trained language models (PLMs) have been successful in high-quality natural language generation. However, the analysis of their generation is not mature: do they acquire generalizable linguistic abstractions, or do they simply memorize and recover substrings of the training data? Especially, few studies focus on domain-specific PLM. In this study, we pre-trained domain-specific GPT-2 models using a limited corpus of Japanese newspaper articles and quantified memorization of training data by comparing them with general Japanese GPT-2 models. Our experiments revealed that domain-specific PLMs sometimes "copy and paste" on a large scale. Furthermore, we replicated the empirical finding that memorization is related to duplication, model size, and prompt length, in Japanese the same as in previous English studies. Our evaluations are relieved from data contamination concerns by focusing on newspaper paywalls, which prevent their use as training data. We hope that our paper encourages a sound discussion such as the security and copyright of PLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge