Probing the contents of semantic representations from text, behavior, and brain data using the psychNorms metabase
Paper and Code
Dec 06, 2024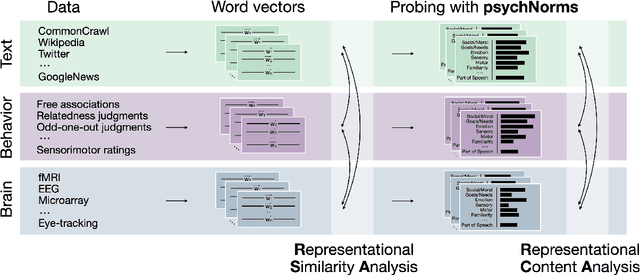
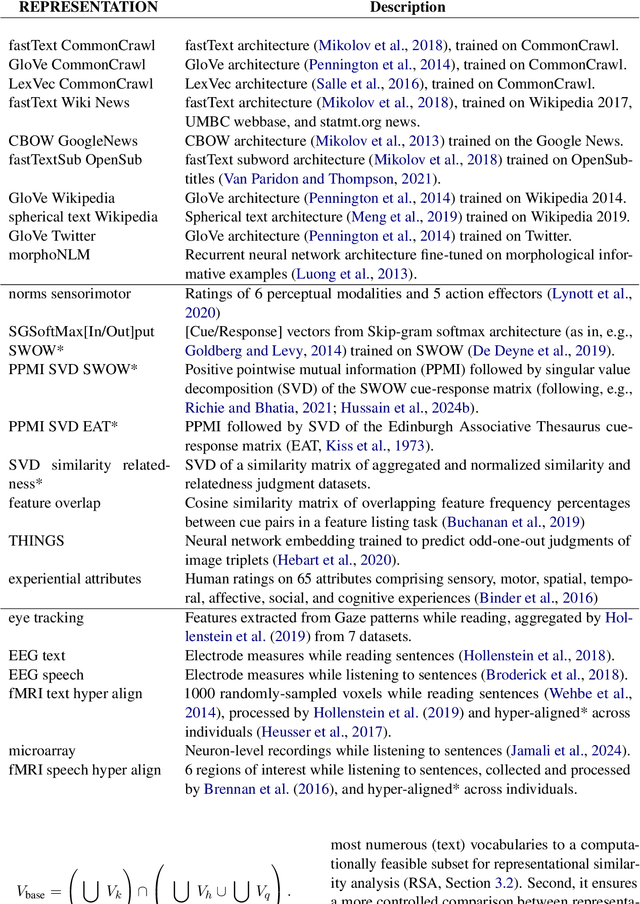
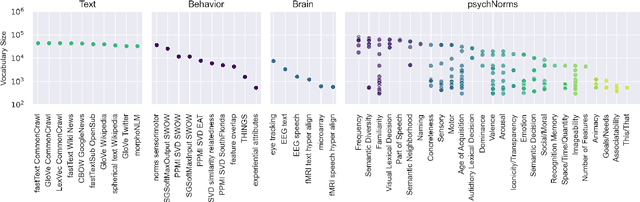
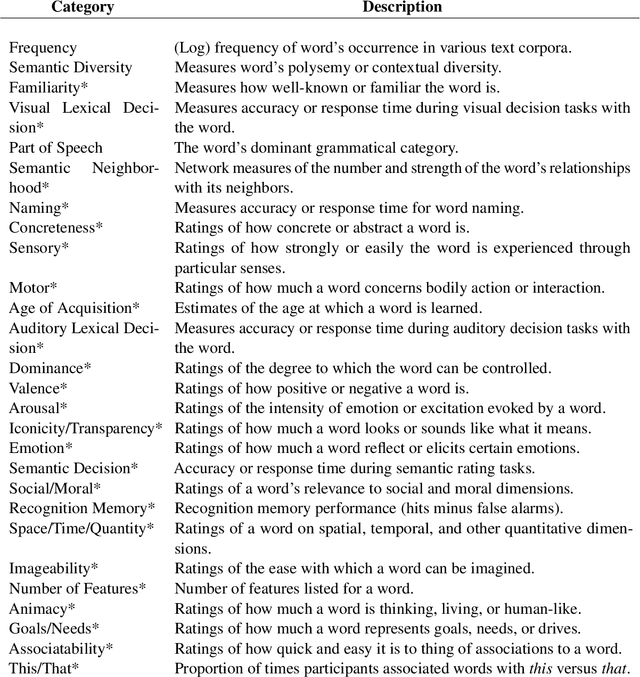
Semantic representations are integral to natural language processing, psycholinguistics, and artificial intelligence. Although often derived from internet text, recent years have seen a rise in the popularity of behavior-based (e.g., free associations) and brain-based (e.g., fMRI) representations, which promise improvements in our ability to measure and model human representations. We carry out the first systematic evaluation of the similarities and differences between semantic representations derived from text, behavior, and brain data. Using representational similarity analysis, we show that word vectors derived from behavior and brain data encode information that differs from their text-derived cousins. Furthermore, drawing on our psychNorms metabase, alongside an interpretability method that we call representational content analysis, we find that, in particular, behavior representations capture unique variance on certain affective, agentic, and socio-moral dimensions. We thus establish behavior as an important complement to text for capturing human representations and behavior. These results are broadly relevant to research aimed at learning human-aligned semantic representations, including work on evaluating and aligning large language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge