Privacy preserving n-party scalar product protocol
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2021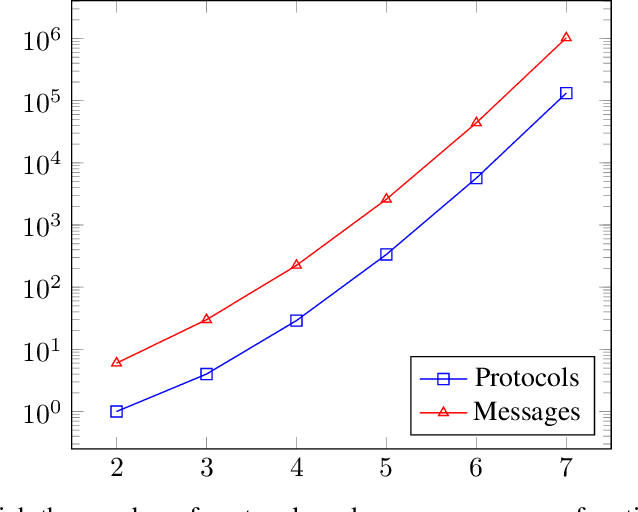
Privacy-preserving machine learning enables the training of models on decentralized datasets without the need to reveal the data, both on horizontal and vertically partitioned data. However, it relies on specialized techniques and algorithms to perform the necessary computations. The privacy preserving scalar product protocol, which enables the dot product of vectors without revealing them, is one popular example for its versatility. Unfortunately, the solutions currently proposed in the literature focus mainly on two-party scenarios, even though scenarios with a higher number of data parties are becoming more relevant. For example when performing analyses that require counting the number of samples which fulfill certain criteria defined across various sites, such as calculating the information gain at a node in a decision tree. In this paper we propose a generalization of the protocol for an arbitrary number of parties, based on an existing two-party method. Our proposed solution relies on a recursive resolution of smaller scalar products. After describing our proposed method, we discuss potential scalability issues. Finally, we describe the privacy guarantees and identify any concerns, as well as comparing the proposed method to the original solution in this aspect.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge