Principal Agent Problem as a Principled Approach to Electronic Counter-Countermeasures in Radar
Paper and Code
Sep 08, 2021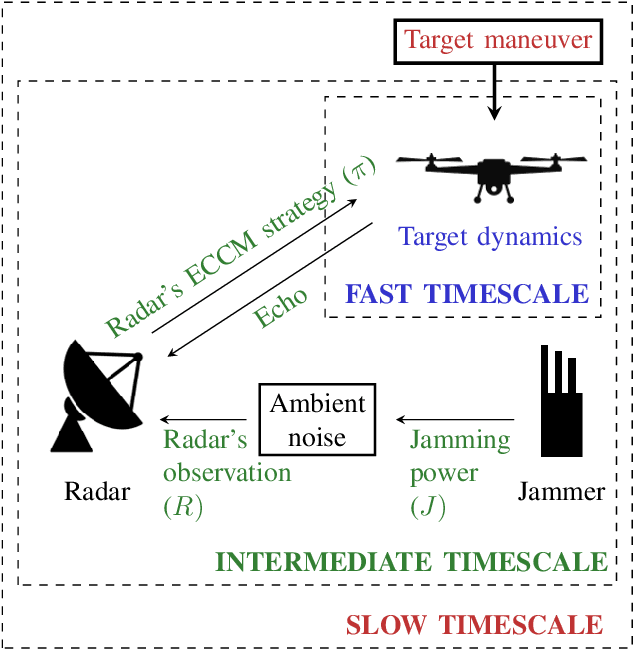
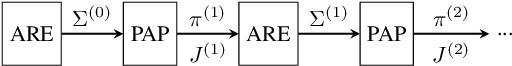
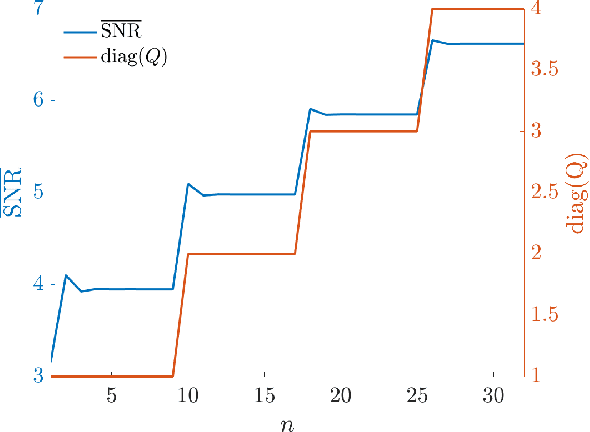
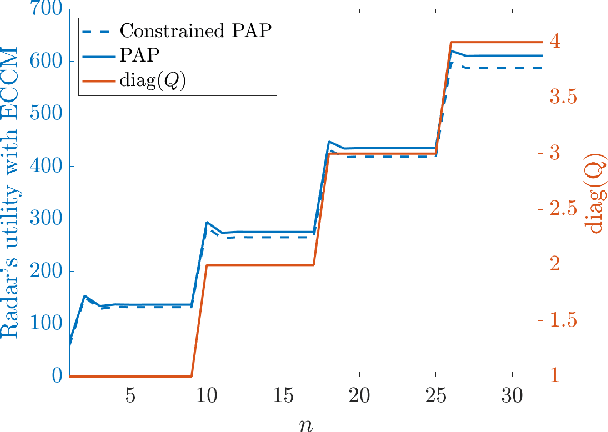
Electronic countermeasures (ECM) against a radar are actions taken by an adversarial jammer to mitigate effective utilization of the electromagnetic spectrum by the radar. On the other hand, electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) are actions taken by the radar to mitigate the impact of electronic countermeasures (ECM) so that the radar can continue to operate effectively. The main idea of this paper is to show that ECCM involving a radar and a jammer can be formulated as a principal-agent problem (PAP) - a problem widely studied in microeconomics. With the radar as the principal and the jammer as the agent, we design a PAP to optimize the radar's ECCM strategy in the presence of a jammer. The radar seeks to optimally trade-off signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the target measurement with the measurement cost: cost for generating radiation power for the pulse to probe the target. We show that for a suitable choice of utility functions, PAP is a convex optimization problem. Further, we analyze the structure of the PAP and provide sufficient conditions under which the optimal solution is an increasing function of the jamming power observed by the radar; this enables computation of the radar's optimal ECCM within the class of increasing affine functions at a low computation cost. Finally, we illustrate the PAP formulation of the radar's ECCM problem via numerical simulations. We also use simulations to study a radar's ECCM problem wherein the radar and the jammer have mismatched information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge