Predicting Shifting Individuals Using Text Mining and Graph Machine Learning on Twitter
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2020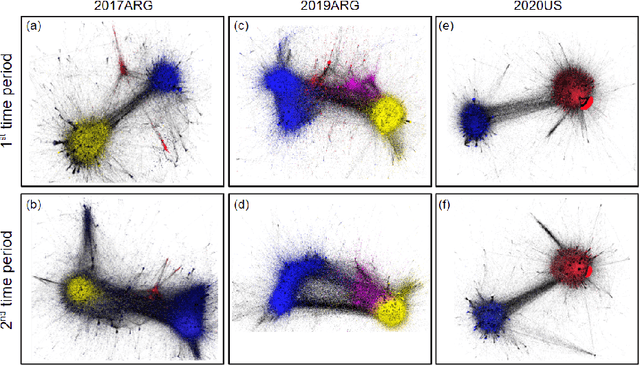
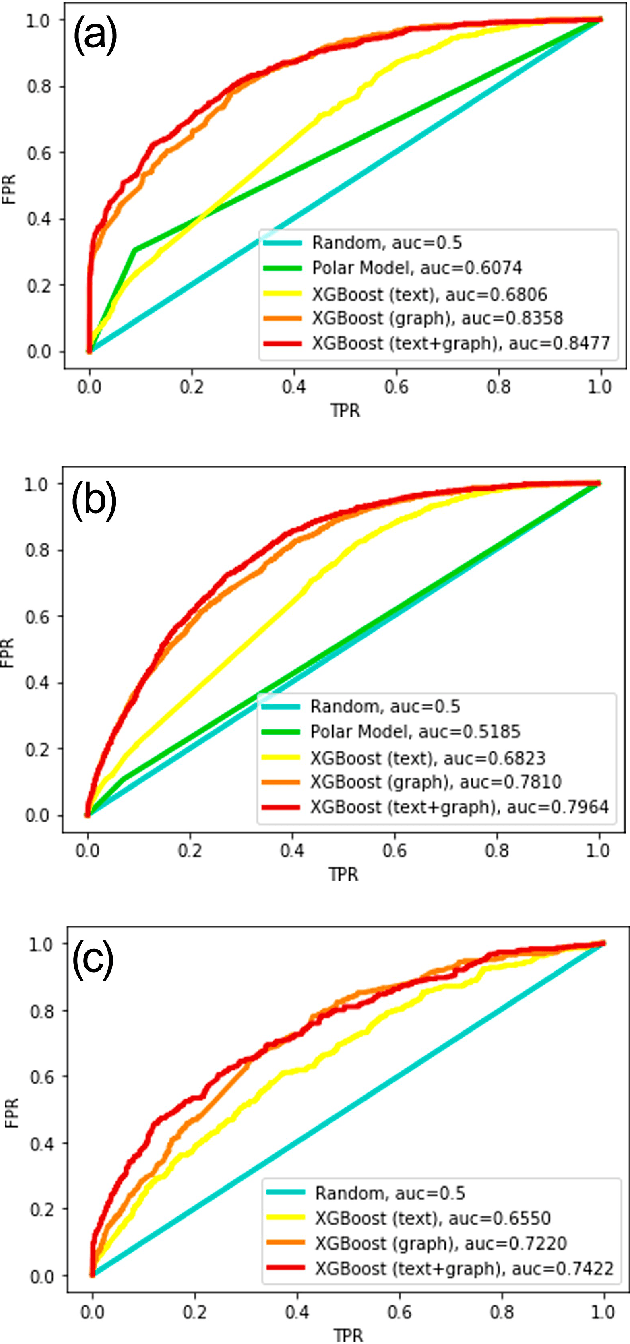
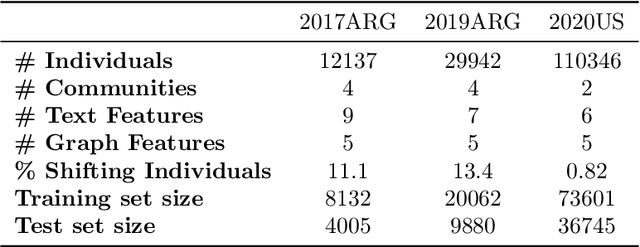
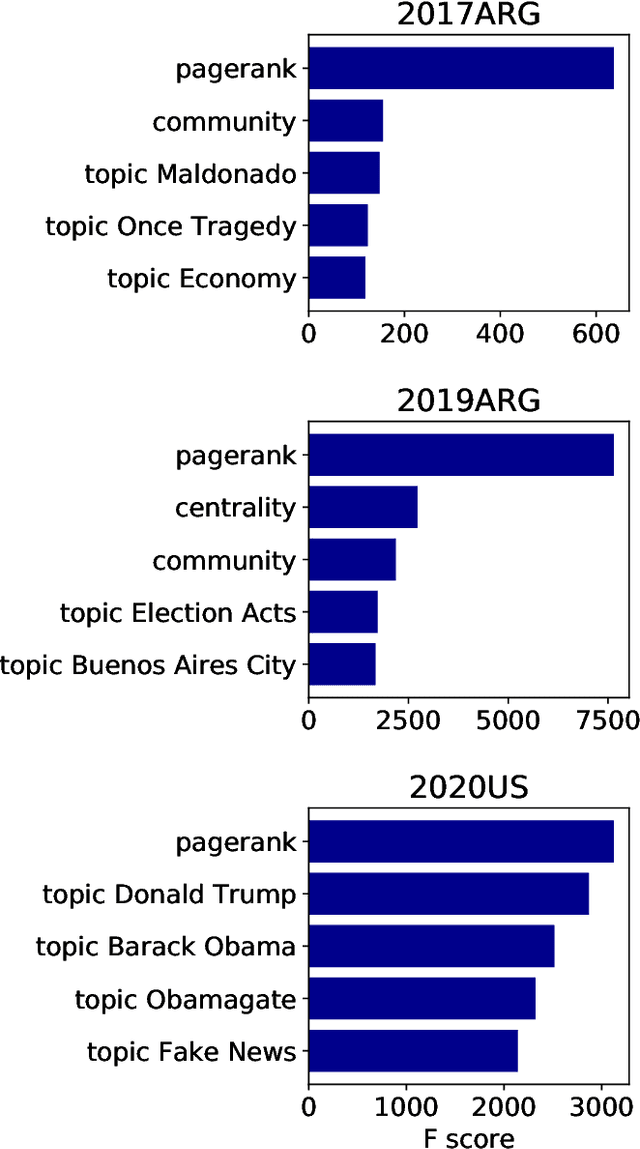
The formation of majorities in public discussions often depends on individuals who shift their opinion over time. The detection and characterization of these type of individuals is therefore extremely important for political analysis of social networks. In this paper, we study changes in individual's affiliations on Twitter using natural language processing techniques and graph machine learning algorithms. In particular, we collected 9 million Twitter messages from 1.5 million users and constructed the retweet networks. We identified communities with explicit political orientation and topics of discussion associated to them which provide the topological representation of the political map on Twitter in the analyzed periods. With that data, we present a machine learning framework for social media users classification which efficiently detects "shifting users" (i.e. users that may change their affiliation over time). Moreover, this machine learning framework allows us to identify not only which topics are more persuasive (using low dimensional topic embedding), but also which individuals are more likely to change their affiliation given their topological properties in a Twitter graph.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge