Predicting Gender via Eye Movements
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2022
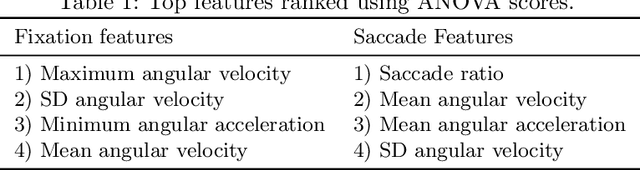

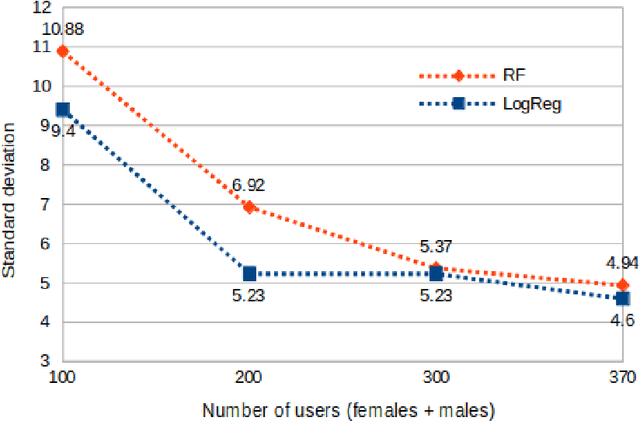
In this paper, we report the first stable results on gender prediction via eye movements. We use a dataset with images of faces as stimuli and with a large number of 370 participants. Stability has two meanings for us: first that we are able to estimate the standard deviation (SD) of a single prediction experiment (it is around 4.1 %); this is achieved by varying the number of participants. And second, we are able to provide a mean accuracy with a very low standard error (SEM): our accuracy is 65.2 %, and the SEM is 0.80 %; this is achieved through many runs of randomly selecting training and test sets for the prediction. Our study shows that two particular classifiers achieve the best accuracies: Random Forests and Logistic Regression. Our results reconfirm previous findings that females are more biased towards the left eyes of the stimuli.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge