Predicting brain age with deep learning from raw imaging data results in a reliable and heritable biomarker
Paper and Code
Dec 08, 2016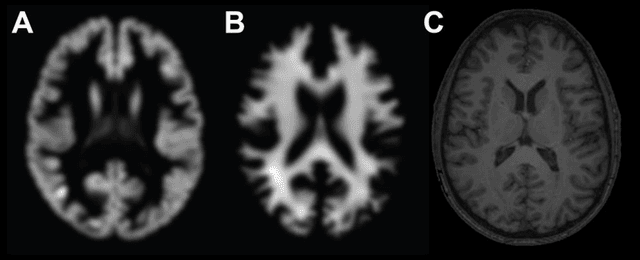
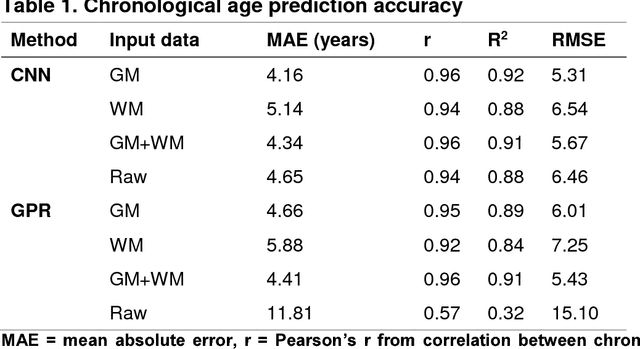
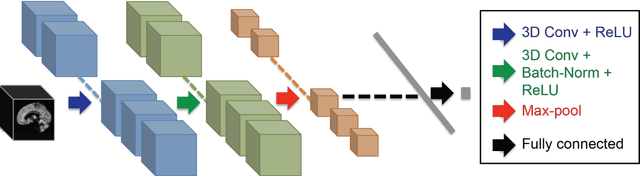
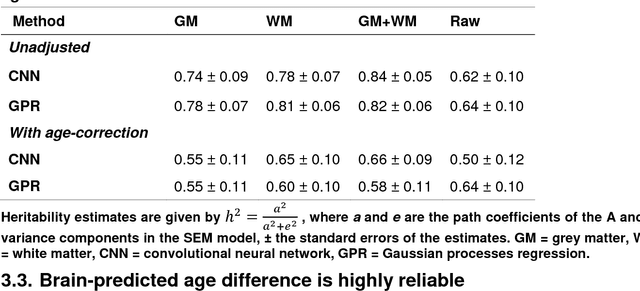
Machine learning analysis of neuroimaging data can accurately predict chronological age in healthy people and deviations from healthy brain ageing have been associated with cognitive impairment and disease. Here we sought to further establish the credentials of "brain-predicted age" as a biomarker of individual differences in the brain ageing process, using a predictive modelling approach based on deep learning, and specifically convolutional neural networks (CNN), and applied to both pre-processed and raw T1-weighted MRI data. Firstly, we aimed to demonstrate the accuracy of CNN brain-predicted age using a large dataset of healthy adults (N = 2001). Next, we sought to establish the heritability of brain-predicted age using a sample of monozygotic and dizygotic female twins (N = 62). Thirdly, we examined the test-retest and multi-centre reliability of brain-predicted age using two samples (within-scanner N = 20; between-scanner N = 11). CNN brain-predicted ages were generated and compared to a Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) approach, on all datasets. Input data were grey matter (GM) or white matter (WM) volumetric maps generated by Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) or raw data. Brain-predicted age represents an accurate, highly reliable and genetically-valid phenotype, that has potential to be used as a biomarker of brain ageing. Moreover, age predictions can be accurately generated on raw T1-MRI data, substantially reducing computation time for novel data, bringing the process closer to giving real-time information on brain health in clinical settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge