Practical Knowledge Distillation: Using DNNs to Beat DNNs
Paper and Code
Mar 01, 2023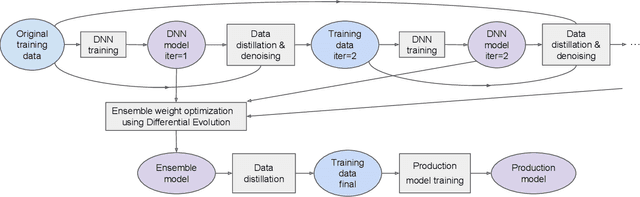
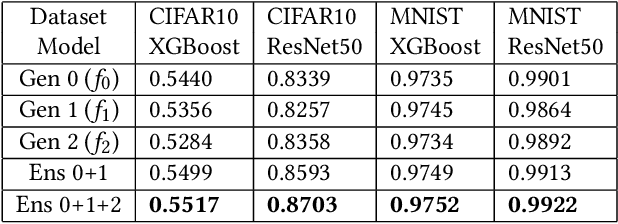
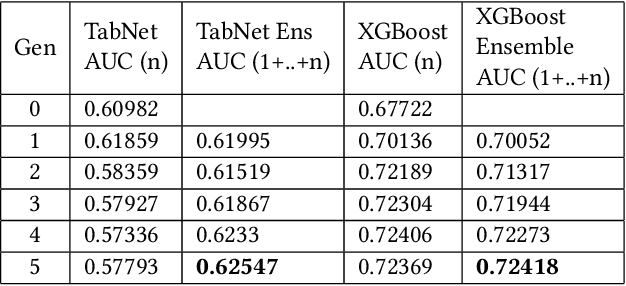
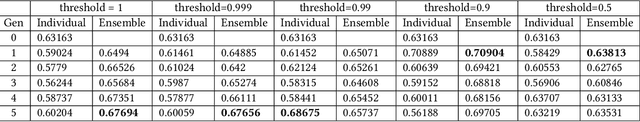
For tabular data sets, we explore data and model distillation, as well as data denoising. These techniques improve both gradient-boosting models and a specialized DNN architecture. While gradient boosting is known to outperform DNNs on tabular data, we close the gap for datasets with 100K+ rows and give DNNs an advantage on small data sets. We extend these results with input-data distillation and optimized ensembling to help DNN performance match or exceed that of gradient boosting. As a theoretical justification of our practical method, we prove its equivalence to classical cross-entropy knowledge distillation. We also qualitatively explain the superiority of DNN ensembles over XGBoost on small data sets. For an industry end-to-end real-time ML platform with 4M production inferences per second, we develop a model-training workflow based on data sampling that distills ensembles of models into a single gradient-boosting model favored for high-performance real-time inference, without performance loss. Empirical evaluation shows that the proposed combination of methods consistently improves model accuracy over prior best models across several production applications deployed worldwide.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge