Practical Fast Gradient Sign Attack against Mammographic Image Classifier
Paper and Code
Jan 27, 2020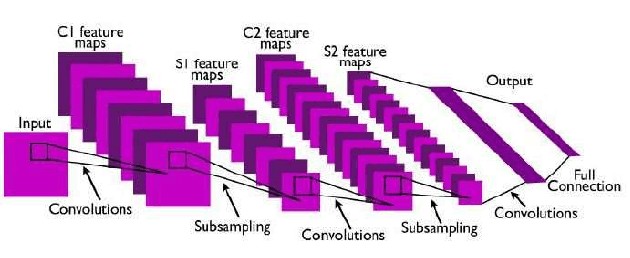
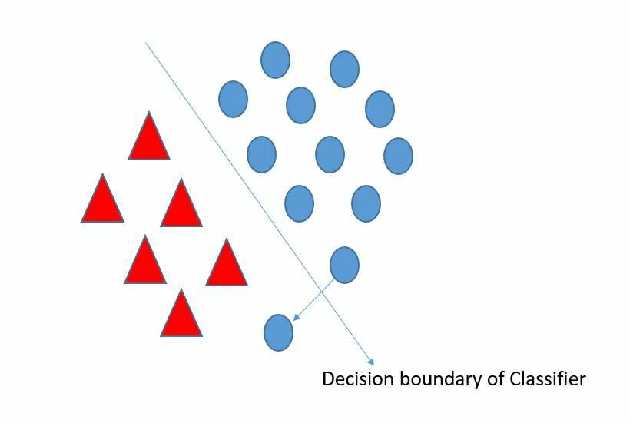
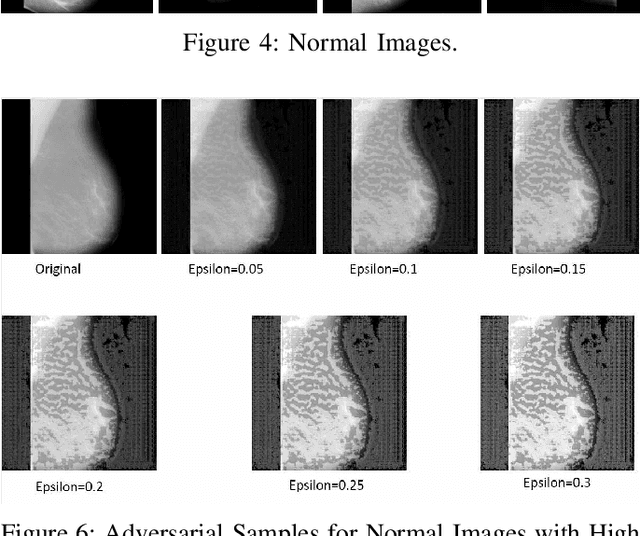
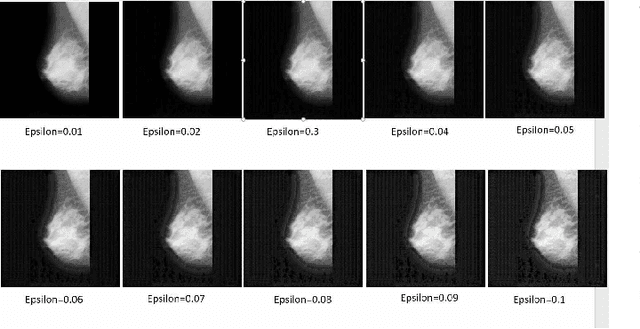
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been a topic of major research for many years. Especially, with the emergence of deep neural network (DNN), these studies have been tremendously successful. Today machines are capable of making faster, more accurate decision than human. Thanks to the great development of machine learning (ML) techniques, ML have been used many different fields such as education, medicine, malware detection, autonomous car etc. In spite of having this degree of interest and much successful research, ML models are still vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Attackers can manipulate clean data in order to fool the ML classifiers to achieve their desire target. For instance; a benign sample can be modified as a malicious sample or a malicious one can be altered as benign while this modification can not be recognized by human observer. This can lead to many financial losses, or serious injuries, even deaths. The motivation behind this paper is that we emphasize this issue and want to raise awareness. Therefore, the security gap of mammographic image classifier against adversarial attack is demonstrated. We use mamographic images to train our model then evaluate our model performance in terms of accuracy. Later on, we poison original dataset and generate adversarial samples that missclassified by the model. We then using structural similarity index (SSIM) analyze similarity between clean images and adversarial images. Finally, we show how successful we are to misuse by using different poisoning factors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge