PooL: Pheromone-inspired Communication Framework forLarge Scale Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Feb 20, 2022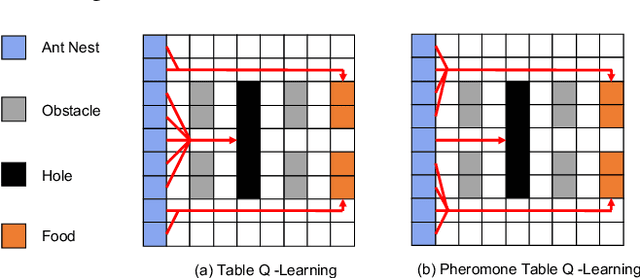
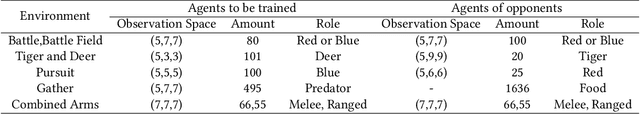
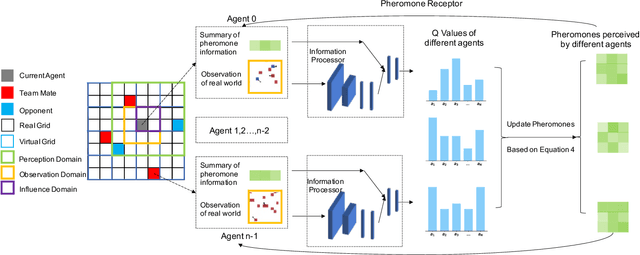
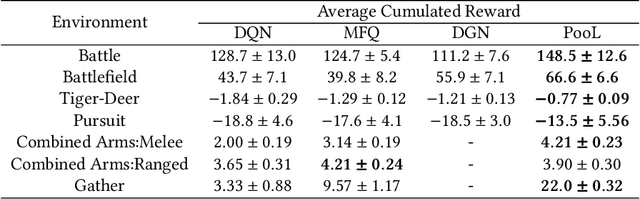
Being difficult to scale poses great problems in multi-agent coordination. Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) algorithms applied in small-scale multi-agent systems are hard to extend to large-scale ones because the latter is far more dynamic and the number of interactions increases exponentially with the growing number of agents. Some swarm intelligence algorithms simulate the release and utilization mechanism of pheromones to control large-scale agent coordination. Inspired by such algorithms, \textbf{PooL}, an \textbf{p}her\textbf{o}m\textbf{o}ne-based indirect communication framework applied to large scale multi-agent reinforcement \textbf{l}earning is proposed in order to solve the large-scale multi-agent coordination problem. Pheromones released by agents of PooL are defined as outputs of most reinforcement learning algorithms, which reflect agents' views of the current environment. The pheromone update mechanism can efficiently organize the information of all agents and simplify the complex interactions among agents into low-dimensional representations. Pheromones perceived by agents can be regarded as a summary of the views of nearby agents which can better reflect the real situation of the environment. Q-Learning is taken as our base model to implement PooL and PooL is evaluated in various large-scale cooperative environments. Experiments show agents can capture effective information through PooL and achieve higher rewards than other state-of-arts methods with lower communication costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge