$pi_t$- Enhancing the Precision of Eye Tracking using Iris Feature Motion Vectors
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2020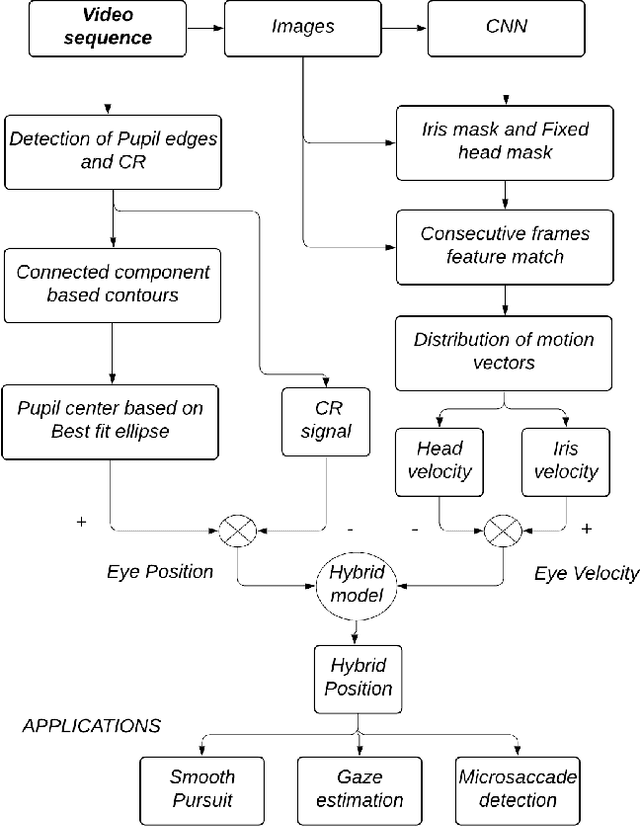

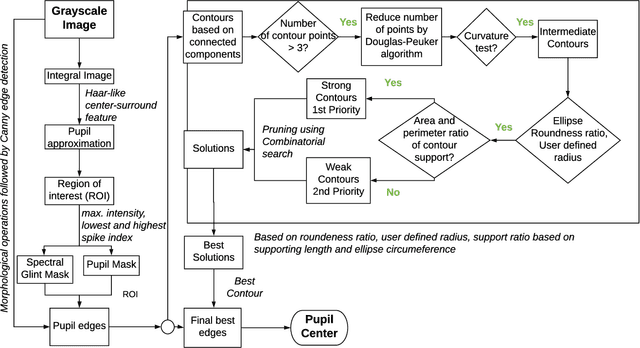

A new high-precision eye-tracking method has been demonstrated recently by tracking the motion of iris features rather than by exploiting pupil edges. While the method provides high precision, it suffers from temporal drift, an inability to track across blinks, and loss of texture matches in the presence of motion blur. In this work, we present a new methodology $pi_t$ to address these issues by optimally combining the information from both iris textures and pupil edges. With this method, we show an improvement in precision (S2S-RMS & STD) of at least 48% and 10% respectively while fixating a series of small targets and following a smoothly moving target. Further, we demonstrate the capability in the identification of microsaccades between targets separated by 0.2-degree.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge