Physics-Compliant Modeling and Scaling Laws of Multi-RIS Aided Systems
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2024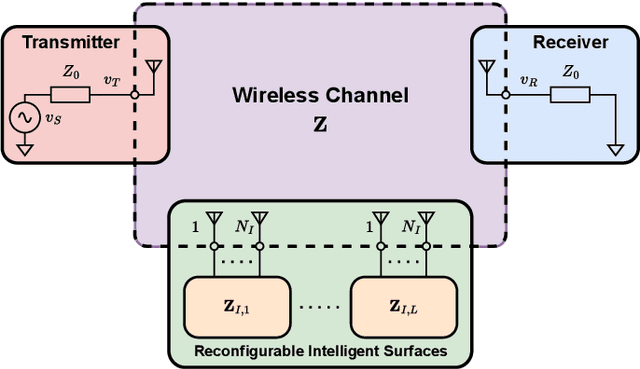
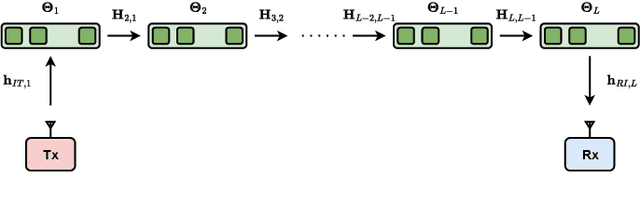
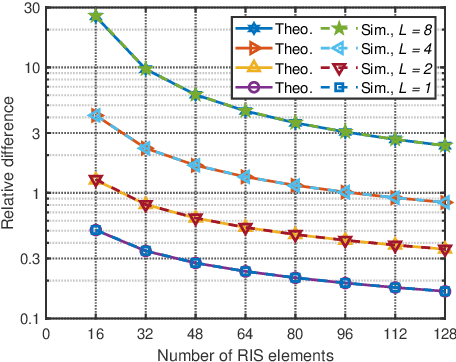
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a revolutionary technology enabling the control of wireless channels and improving coverage in wireless networks. To further extend coverage, multi-RIS aided systems have been explored, where multiple RISs steer the signal toward the receiver via a multi-hop path. However, deriving a physics-compliant channel model for multi-RIS aided systems is still an open problem. In this study, we fill this gap by modeling multi-RIS aided systems through multiport network theory, and deriving the scaling law of the physics-compliant channel gain. The derived physics-compliant channel model differs from the widely used model, where the structural scattering of the RISs is neglected. Theoretical insights, validated by numerical results, show a significant discrepancy between the physics-compliant and the widely used models. This discrepancy increases with the number of RISs and decreases with the number of RIS elements, reaching 200% in a system with eight RISs with 128 elements each.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge