Physical Modeling using Recurrent Neural Networks with Fast Convolutional Layers
Paper and Code
Apr 21, 2022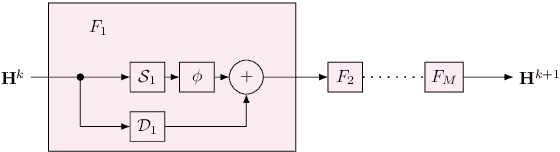

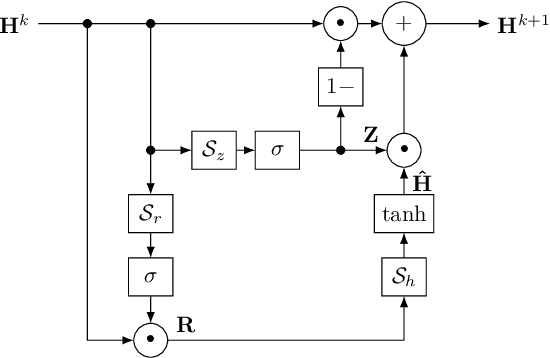
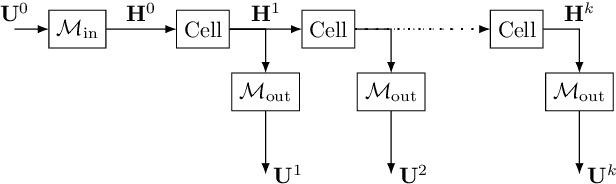
Discrete-time modeling of acoustic, mechanical and electrical systems is a prominent topic in the musical signal processing literature. Such models are mostly derived by discretizing a mathematical model, given in terms of ordinary or partial differential equations, using established techniques. Recent work has applied the techniques of machine-learning to construct such models automatically from data for the case of systems which have lumped states described by scalar values, such as electrical circuits. In this work, we examine how similar techniques are able to construct models of systems which have spatially distributed rather than lumped states. We describe several novel recurrent neural network structures, and show how they can be thought of as an extension of modal techniques. As a proof of concept, we generate synthetic data for three physical systems and show that the proposed network structures can be trained with this data to reproduce the behavior of these systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge