Optical character recognition quality affects perceived usefulness of historical newspaper clippings
Paper and Code
Jun 01, 2022

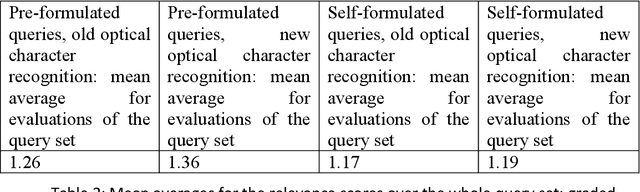

Introduction. We study effect of different quality optical character recognition in interactive information retrieval with a collection of one digitized historical Finnish newspaper. Method. This study is based on the simulated interactive information retrieval work task model. Thirty-two users made searches to an article collection of Finnish newspaper Uusi Suometar 1869-1918 with ca. 1.45 million auto segmented articles. Our article search database had two versions of each article with different quality optical character recognition. Each user performed six pre-formulated and six self-formulated short queries and evaluated subjectively the top-10 results using graded relevance scale of 0-3 without knowing about the optical character recognition quality differences of the otherwise identical articles. Analysis. Analysis of the user evaluations was performed by comparing mean averages of evaluations scores in user sessions. Differences of query results were detected by analysing lengths of returned articles in pre-formulated and self-formulated queries and number of different documents retrieved overall in these two sessions. Results. The main result of the study is that improved optical character recognition quality affects perceived usefulness of historical newspaper articles positively. Conclusions. We were able to show that improvement in optical character recognition quality of documents leads to higher mean relevance evaluation scores of query results in our historical newspaper collection. To the best of our knowledge this simulated interactive user-task is the first one showing empirically that users' subjective relevance assessments are affected by a change in the quality of optically read text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge