On the universality of cognitive tests
Paper and Code
May 09, 2013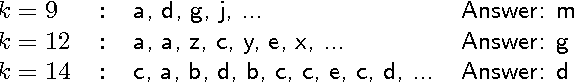
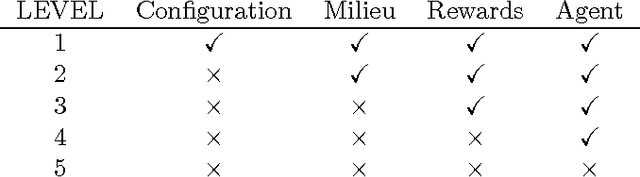
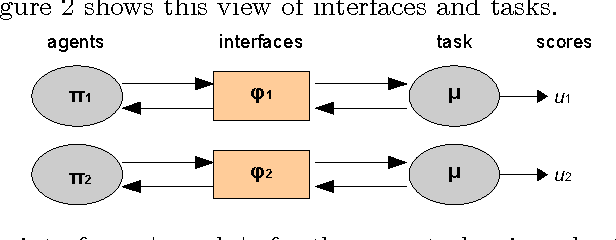

The analysis of the adaptive behaviour of many different kinds of systems such as humans, animals and machines, requires more general ways of assessing their cognitive abilities. This need is strengthened by increasingly more tasks being analysed for and completed by a wider diversity of systems, including swarms and hybrids. The notion of universal test has recently emerged in the context of machine intelligence evaluation as a way to define and use the same cognitive test for a variety of systems, using some principled tasks and adapting the interface to each particular subject. However, how far can universal tests be taken? This paper analyses this question in terms of subjects, environments, space-time resolution, rewards and interfaces. This leads to a number of findings, insights and caveats, according to several levels where universal tests may be progressively more difficult to conceive, implement and administer. One of the most significant contributions is given by the realisation that more universal tests are defined as maximisations of less universal tests for a variety of configurations. This means that universal tests must be necessarily adaptive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge