On the role of features in vertex nomination: Content and context together are better
Paper and Code
May 06, 2020
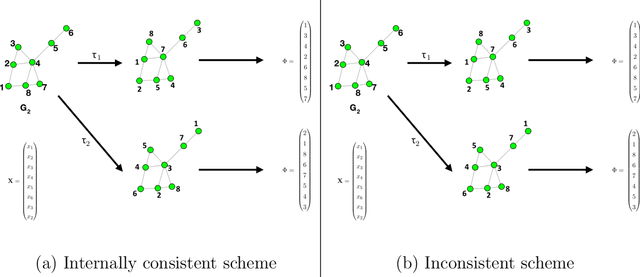
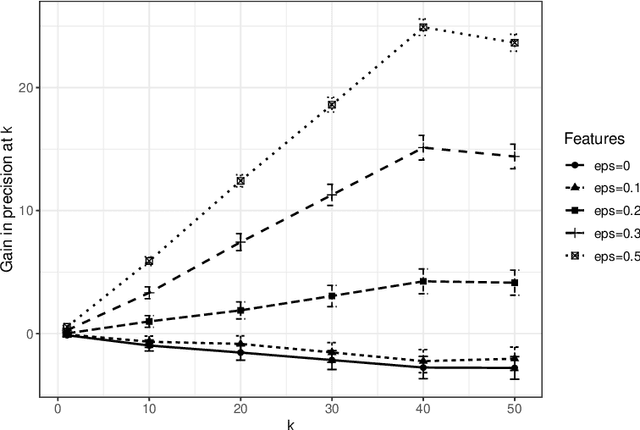
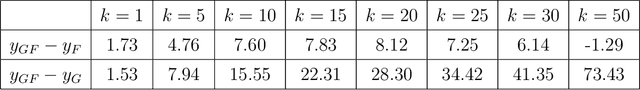
Vertex nomination is a lightly-supervised network information retrieval (IR) task in which vertices of interest in one graph are used to query a second graph to discover vertices of interest in the second graph. Similar to other IR tasks, the output of a vertex nomination scheme is a ranked list of the vertices in the second graph, with the heretofore unknown vertices of interest ideally concentrating at the top of the list. Vertex nomination schemes provide a useful suite of tools for efficiently mining complex networks for pertinent information. In this paper, we explore, both theoretically and practically, the dual roles of content (i.e., edge and vertex attributes) and context (i.e., network topology) in vertex nomination. We provide necessary and sufficient conditions under which vertex nomination schemes that leverage both content and context outperform schemes that leverage only content or context separately. While the joint utility of both content and context has been demonstrated empirically in the literature, the framework presented in this paper provides a novel theoretical basis for understanding the potential complementary roles of network features and topology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge