On the Efficiency of Subclass Knowledge Distillation in Classification Tasks
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2021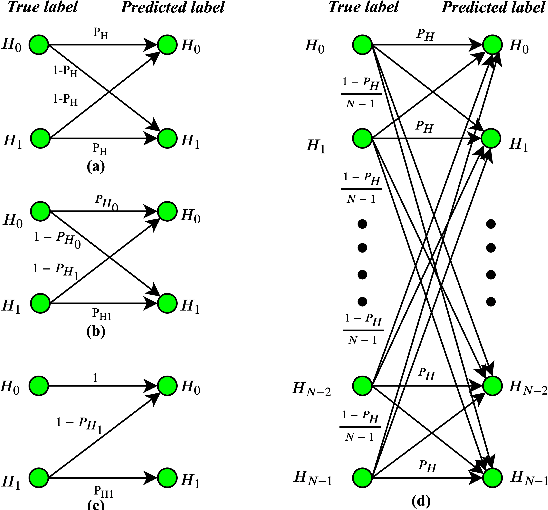
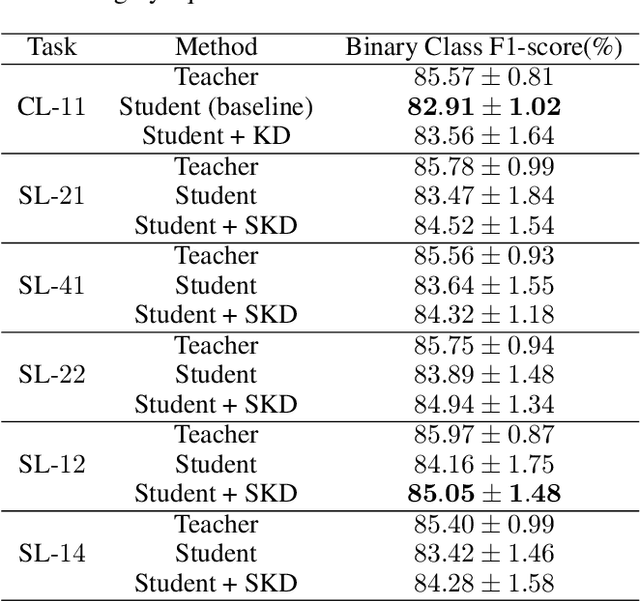
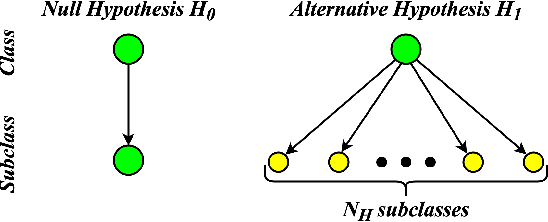

This work introduces a novel knowledge distillation framework for classification tasks where information on existing subclasses is available and taken into consideration. In classification tasks with a small number of classes or binary detection (two classes) the amount of information transferred from the teacher to the student network is restricted, thus limiting the utility of knowledge distillation. Performance can be improved by leveraging information about possible subclasses within the available classes in the classification task. To that end, we propose the so-called Subclass Knowledge Distillation (SKD) framework, which is the process of transferring the subclasses' prediction knowledge from a large teacher model into a smaller student one. Through SKD, additional meaningful information which is not in the teacher's class logits but exists in subclasses (e.g., similarities inside classes) will be conveyed to the student and boost its performance. Mathematically, we measure how many extra information bits the teacher can provide for the student via SKD framework. The framework developed is evaluated in clinical application, namely colorectal polyp binary classification. In this application, clinician-provided annotations are used to define subclasses based on the annotation label's variability in a curriculum style of learning. A lightweight, low complexity student trained with the proposed framework achieves an F1-score of 85.05%, an improvement of 2.14% and 1.49% gain over the student that trains without and with conventional knowledge distillation, respectively. These results show that the extra subclasses' knowledge (i.e., 0.4656 label bits per training sample in our experiment) can provide more information about the teacher generalization, and therefore SKD can benefit from using more information to increase the student performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge