On Computability, Learnability and Extractability of Finite State Machines from Recurrent Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Sep 10, 2020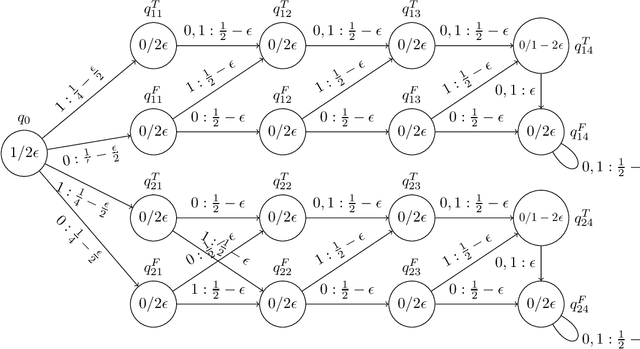

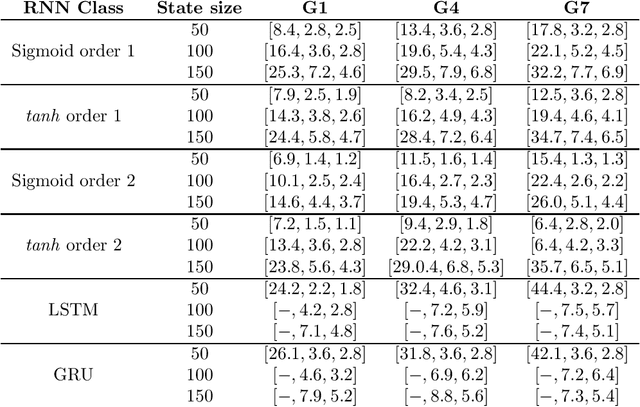
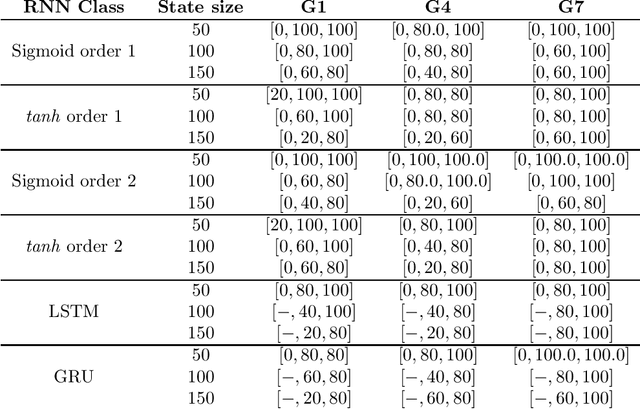
This work aims at shedding some light on connections between finite state machines (FSMs), and recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Examined connections in this master's thesis is threefold: the extractability of finite state machines from recurrent neural networks, learnability aspects and computationnal links. With respect to the former, the long-standing clustering hypothesis of RNN hidden state space when trained to recognize regular languages was explored, and new insights into this hypothesis through the lens of recent advances of the generalization theory of Deep Learning are provided. As for learnability, an extension of the active learning framework better suited to the problem of approximating RNNs with FSMs is proposed, with the aim of better formalizing the problem of RNN approximation by FSMs. Theoretical analysis of two possible scenarions in this framework were performed. With regard to computability, new computational results on the distance and the equivalence problem between RNNs trained as language models and different types of weighted finite state machines were given.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge