Noise Detection with Spectator Qubits and Quantum Feature Engineering
Paper and Code
Mar 24, 2021
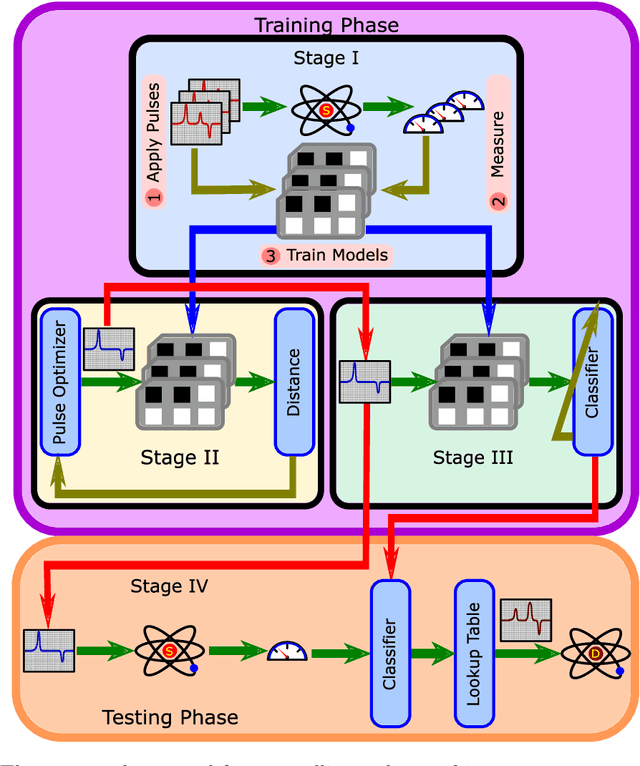
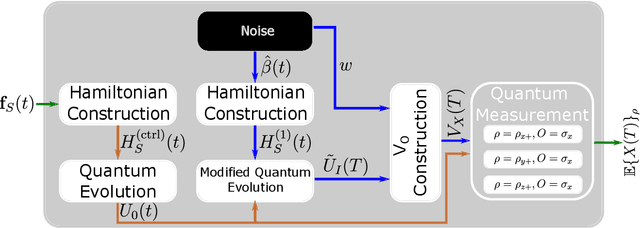
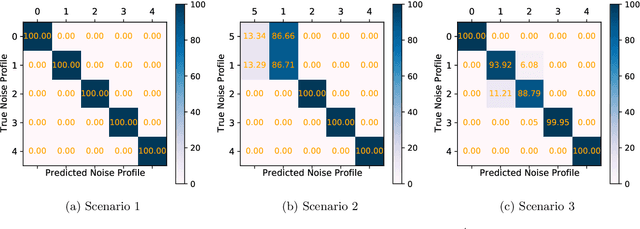
Designing optimal control pulses that drive a noisy qubit to a target state is a challenging and crucial task for quantum engineering. In a situation where the properties of the quantum noise affecting the system are dynamic, a periodic characterization procedure is essential to ensure the models are updated. As a result, the operation of the qubit is disrupted frequently. In this paper, we propose a protocol that addresses this challenge by making use of a spectator qubit to monitor the noise in real-time. We develop a quantum machine-learning-based quantum feature engineering approach for designing the protocol. The complexity of the protocol is front-loaded in a characterization phase, which allow real-time execution during the quantum computations. We present the results of numerical simulations that showcase the favorable performance of the protocol.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge