Negotiative Alignment: Embracing Disagreement to Achieve Fairer Outcomes -- Insights from Urban Studies
Paper and Code
Mar 16, 2025


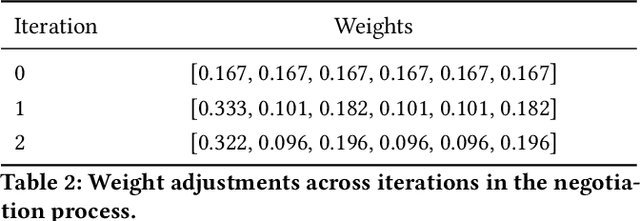
Cities are not monolithic; they are arenas of negotiation among groups that hold varying needs, values, and experiences. Conventional methods of urban assessment -- from standardized surveys to AI-driven evaluations -- frequently rely on a single consensus metric (e.g., an average measure of inclusivity or safety). Although such aggregations simplify design decisions, they risk obscuring the distinct perspectives of marginalized populations. In this paper, we present findings from a community-centered study in Montreal involving 35 residents with diverse demographic and social identities, particularly wheelchair users, seniors, and LGBTQIA2+ individuals. Using rating and ranking tasks on 20 urban sites, we observe that disagreements are systematic rather than random, reflecting structural inequalities, differing cultural values, and personal experiences of safety and accessibility. Based on these empirical insights, we propose negotiative alignment, an AI framework that treats disagreement as an essential input to be preserved, analyzed, and addressed. Negotiative alignment builds on pluralistic models by dynamically updating stakeholder preferences through multi-agent negotiation mechanisms, ensuring no single perspective is marginalized. We outline how this framework can be integrated into urban analytics -- and other decision-making contexts -- to retain minority viewpoints, adapt to changing stakeholder concerns, and enhance fairness and accountability. The study demonstrates that preserving and engaging with disagreement, rather than striving for an artificial consensus, can produce more equitable and responsive AI-driven outcomes in urban design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge