MutualGraphNet: A novel model for motor imagery classification
Paper and Code
Sep 02, 2021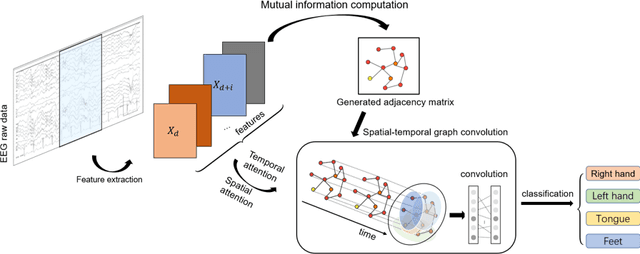
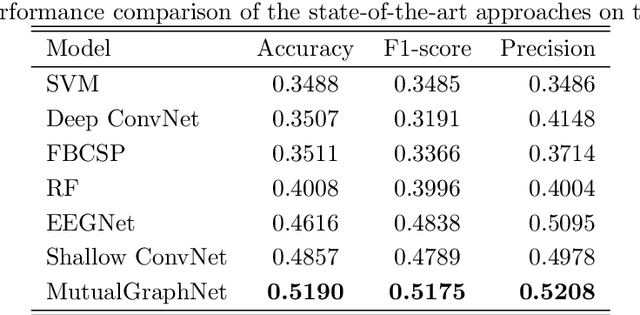
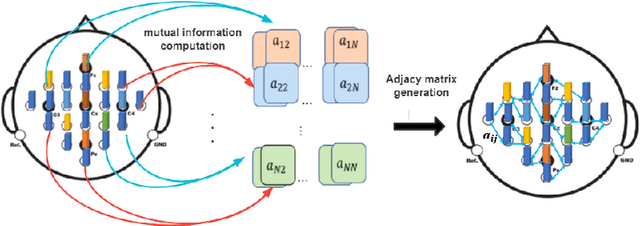
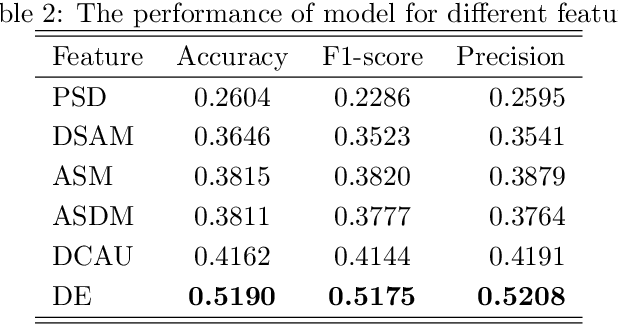
Motor imagery classification is of great significance to humans with mobility impairments, and how to extract and utilize the effective features from motor imagery electroencephalogram(EEG) channels has always been the focus of attention. There are many different methods for the motor imagery classification, but the limited understanding on human brain requires more effective methods for extracting the features of EEG data. Graph neural networks(GNNs) have demonstrated its effectiveness in classifying graph structures; and the use of GNN provides new possibilities for brain structure connection feature extraction. In this paper we propose a novel graph neural network based on the mutual information of the raw EEG channels called MutualGraphNet. We use the mutual information as the adjacency matrix combined with the spatial temporal graph convolution network(ST-GCN) could extract the transition rules of the motor imagery electroencephalogram(EEG) channels data more effectively. Experiments are conducted on motor imagery EEG data set and we compare our model with the current state-of-the-art approaches and the results suggest that MutualGraphNet is robust enough to learn the interpretable features and outperforms the current state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge