Multiple access for near-field communications: SDMA or LDMA?
Paper and Code
Aug 12, 2022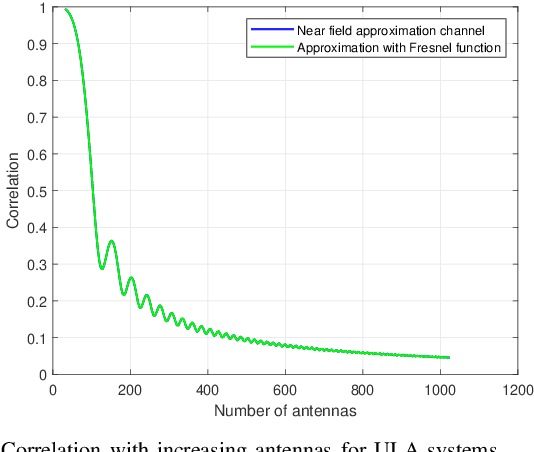
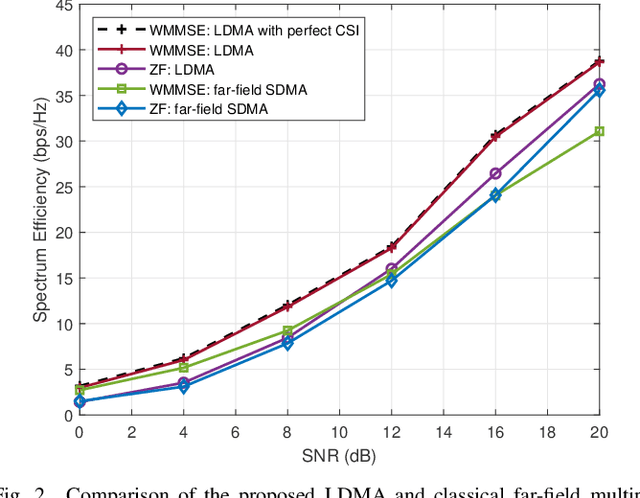
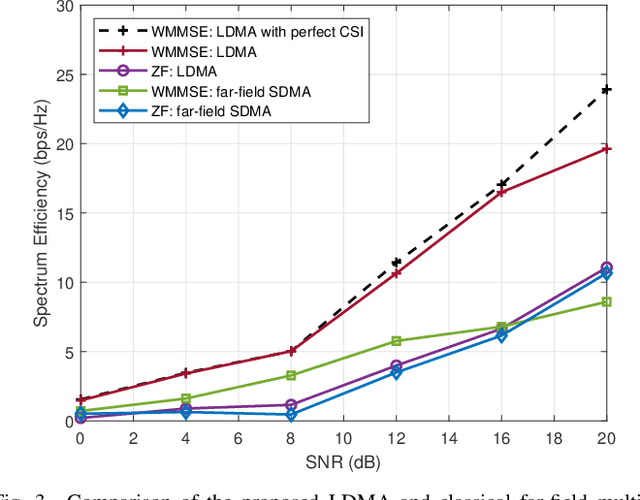
Spatial division multiple access (SDMA) is essential in supporting multiple user transmissions in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communications. Classical 5G massive MIMO SDMA relies on the orthogonality in far-field areas to distinguish multiple users residing at different angles, which fails to make full use of the spatial resources. With the dramatically increasing number of antennas, the extremely large-scale antenna array (ELAA) introduces the additional spatial resolution in the distance domain, which provides a new dimension for enhancing multiple accessibility in the near-field region. In this paper, we propose the concept of location division multiple access (LDMA), which elaborately exploit the spatial resources to serve multiple users at different locations. Specifically, unlike classical far-field beamsteering vectors which focus on specific angles, near-field beamfocusing vectors are capable of focusing on specific locations with managed leakage energy on other locations. The near-field focusing property could be leveraged to mitigate the interference from users at the same angle to enhance the multiple accessibility. Similar to the asymptotic angular orthogonality of far-field beamsteering vectors, the asymptotic orthogonality of near-field beamfocusing in the distance domain is investigated. Near-field codebook design is critical to support multiple transmission services. An alternate algorithm based on generalized Lloyd algorithm (GLA) and heuristic spherical sampling method is proposed for uniform planar array (UPA) codebook design. Based on the near-field codebook, LDMA scheme is investigated, comprising the beam training, uplink channel estimation and downlink transmission procedure. Simulation results verify the superiority of proposed LDMA scheme on spectral efficiency over different scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge