MultiCheXNet: A Multi-Task Learning Deep Network For Pneumonia-like Diseases Diagnosis From X-ray Scans
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2020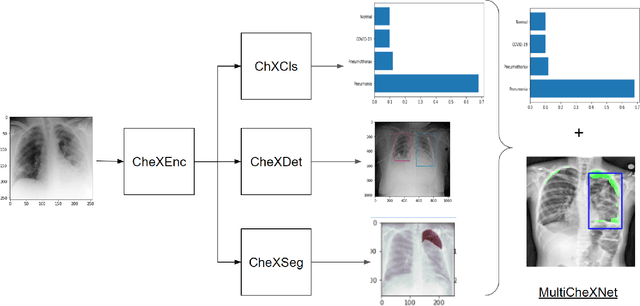



We present MultiCheXNet, an end-to-end Multi-task learning model, that is able to take advantage of different X-rays data sets of Pneumonia-like diseases in one neural architecture, performing three tasks at the same time; diagnosis, segmentation and localization. The common encoder in our architecture can capture useful common features present in the different tasks. The common encoder has another advantage of efficient computations, which speeds up the inference time compared to separate models. The specialized decoders heads can then capture the task-specific features. We employ teacher forcing to address the issue of negative samples that hurt the segmentation and localization performance. Finally,we employ transfer learning to fine tune the classifier on unseen pneumonia-like diseases. The MTL architecture can be trained on joint or dis-joint labeled data sets. The training of the architecture follows a carefully designed protocol, that pre trains different sub-models on specialized datasets, before being integrated in the joint MTL model. Our experimental setup involves variety of data sets, where the baseline performance of the 3 tasks is compared to the MTL architecture performance. Moreover, we evaluate the transfer learning mode to COVID-19 data set,both from individual classifier model, and from MTL architecture classification head.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge