Multi-task Feature Enhancement Network for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment
Paper and Code
Nov 12, 2024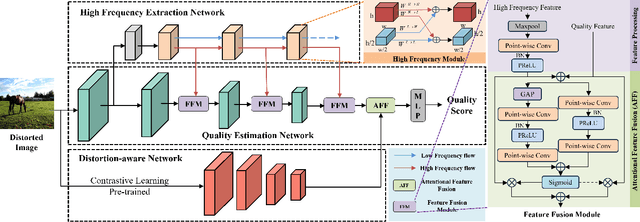

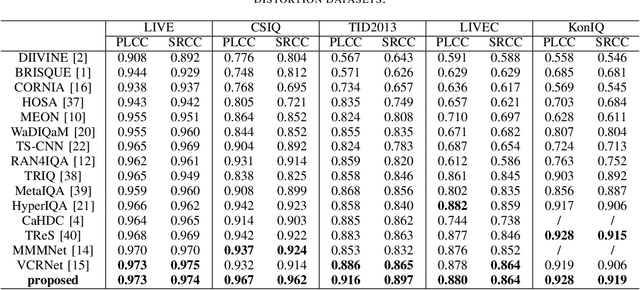
Due to the scarcity of labeled samples in Image Quality Assessment (IQA) datasets, numerous recent studies have proposed multi-task based strategies, which explore feature information from other tasks or domains to boost the IQA task. Nevertheless, multi-task strategies based No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) methods encounter several challenges. First, existing methods have not explicitly exploited texture details, which significantly influence the image quality. Second, multi-task methods conventionally integrate features through simple operations such as addition or concatenation, thereby diminishing the network's capacity to accurately represent distorted features. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a novel multi-task NR-IQA framework. Our framework consists of three key components: a high-frequency extraction network, a quality estimation network, and a distortion-aware network. The high-frequency extraction network is designed to guide the model's focus towards high-frequency information, which is highly related to the texture details. Meanwhile, the distortion-aware network extracts distortion-related features to distinguish different distortion types. To effectively integrate features from different tasks, a feature fusion module is developed based on an attention mechanism. Empirical results from five standard IQA databases confirm that our method not only achieves high performance but also exhibits robust generalization ability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge