Multi-objective Reinforcement learning from AI Feedback
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2024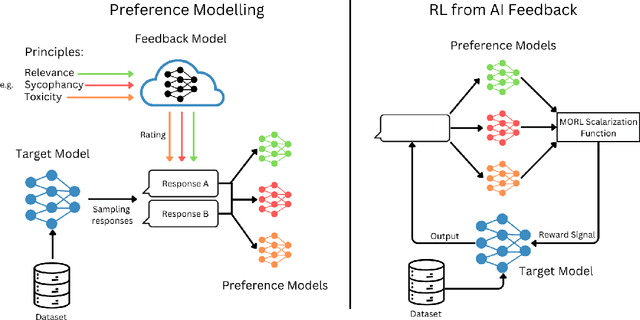
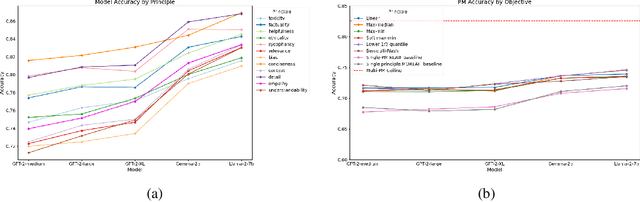

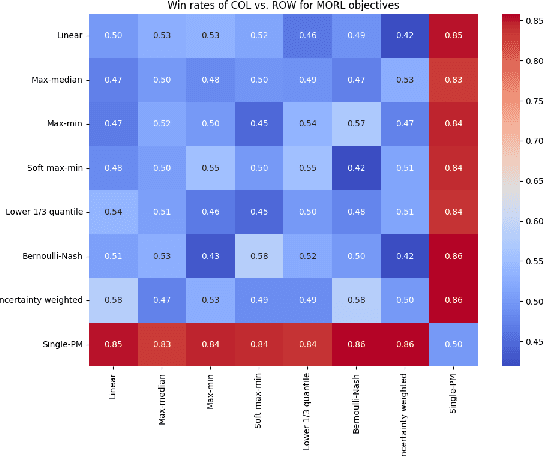
This paper presents Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (MORLAIF), a novel approach to improving the alignment and performance of language models trained using reinforcement learning from AI feedback (RLAIF). In contrast to standard approaches that train a single preference model to represent all human preferences, MORLAIF decomposes this task into multiple simpler principles, such as toxicity, factuality, and sycophancy. Separate preference models are trained for each principle using feedback from GPT-3.5-Turbo. These preference model scores are then combined using different scalarization functions to provide a reward signal for Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) training of the target language model. Our experiments indicate that MORLAIF outperforms the standard RLAIF baselines and that MORLAIF can be used to align larger language models using smaller ones. Surprisingly, the choice of scalarization function does not appear to significantly impact the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge