Multi-Link Vehicular Wireless Channel Modelling: Impact of Large Obstructing Vehicles
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2021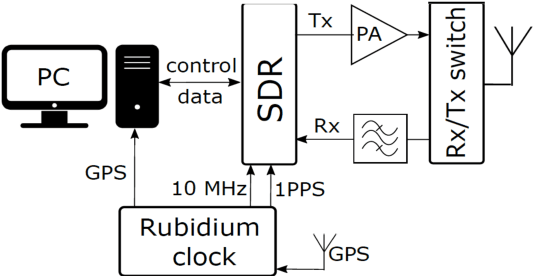



Multi-node channel sounding simultaneously captures multiple channel transfer functions in complex scenarios. It ensures that measurement conditions are identical for all observed links. This is particularly beneficial in analyzing highly-dynamic vehicular communication scenarios, where the measurement conditions and wireless channel statistics change rapidly. We present the first fully mobile multi-node vehicular wireless channel sounding results. We analyze the impact of a double-decker bus on the channel statistics in two measurement scenarios. The measurement data is used to calibrate an OpenStreetMap geometry-based stochastic channel model and include a more accurate modeling for large vehicles, absent from previous models. We validate our model using a link-level emulation, demonstrating a good match with measurement data. Finally, we propose a relaying scenario and test it on link-level by comparing the time-variant error rates of measured links.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge