Multi-group Learning for Hierarchical Groups
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2024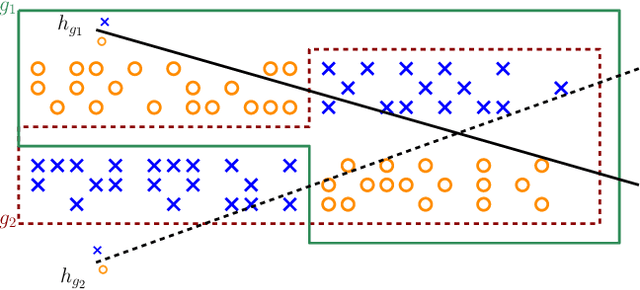

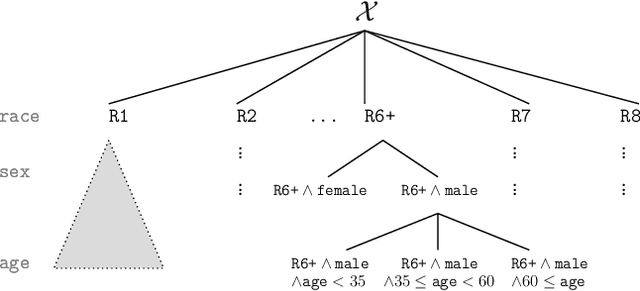
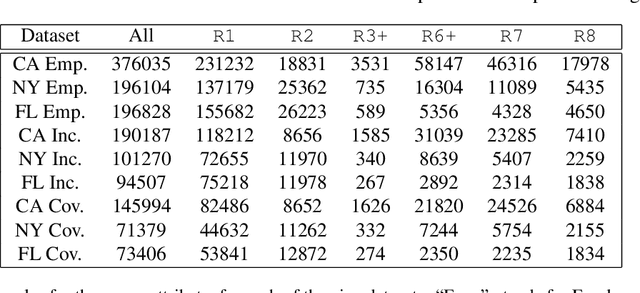
The multi-group learning model formalizes the learning scenario in which a single predictor must generalize well on multiple, possibly overlapping subgroups of interest. We extend the study of multi-group learning to the natural case where the groups are hierarchically structured. We design an algorithm for this setting that outputs an interpretable and deterministic decision tree predictor with near-optimal sample complexity. We then conduct an empirical evaluation of our algorithm and find that it achieves attractive generalization properties on real datasets with hierarchical group structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge