Multi-fidelity Bayesian Optimisation of Syngas Fermentation Simulators
Paper and Code
Nov 06, 2023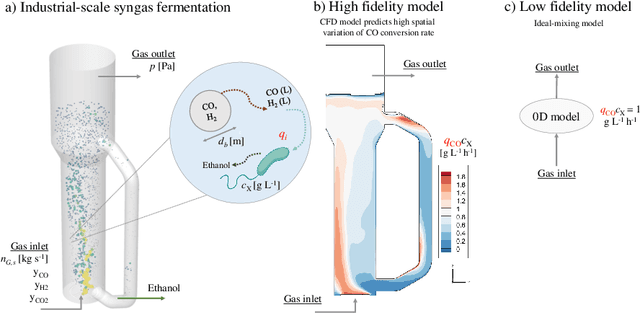
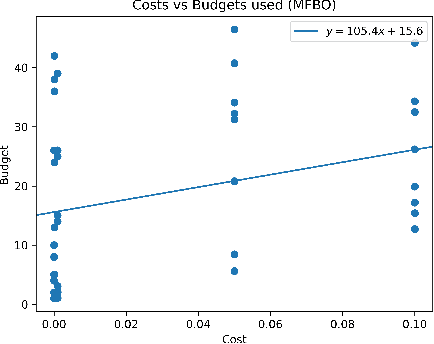
A Bayesian optimization approach for maximizing the gas conversion rate in an industrial-scale bioreactor for syngas fermentation is presented. We have access to a high-fidelity, computational fluid dynamic (CFD) reactor model and a low-fidelity ideal-mixing-based reactor model. The goal is to maximize the gas conversion rate, with respect to the input variables (e.g., pressure, biomass concentration, gas flow rate). Due to the high cost of the CFD reactor model, a multi-fidelity Bayesian optimization algorithm is adopted to solve the optimization problem using both high and low fidelities. We first describe the problem in the context of syngas fermentation followed by our approach to solving simulator optimization using multiple fidelities. We discuss concerns regarding significant differences in fidelity cost and their impact on fidelity sampling and conclude with a discussion on the integration of real-world fermentation data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge