Modelling Contractual Arguments
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2001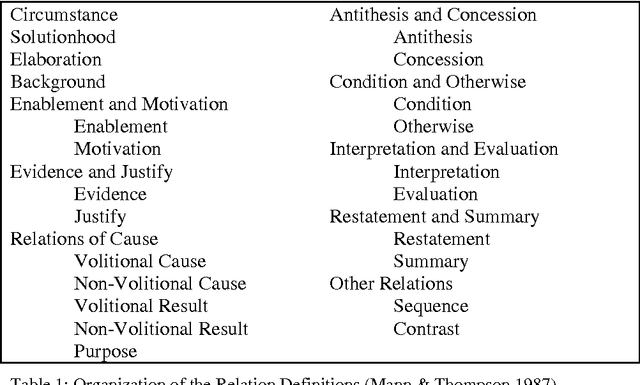
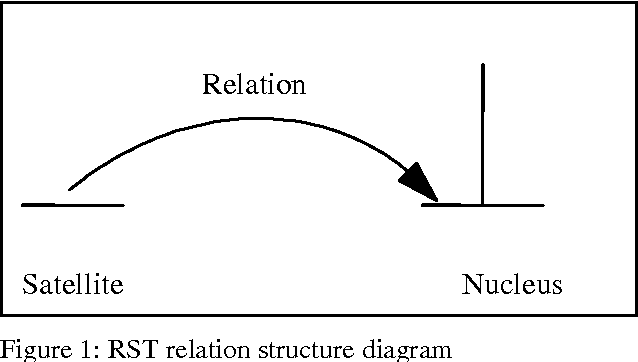
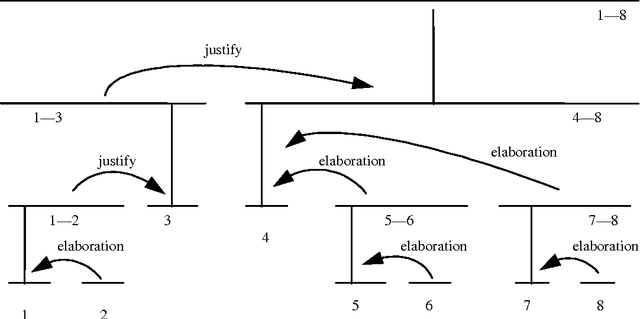
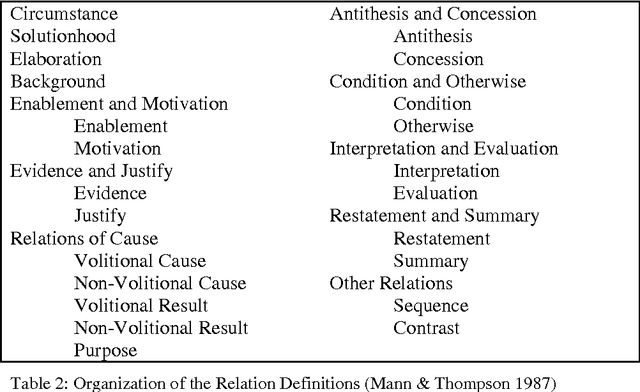
One influential approach to assessing the "goodness" of arguments is offered by the Pragma-Dialectical school (p-d) (Eemeren & Grootendorst 1992). This can be compared with Rhetorical Structure Theory (RST) (Mann & Thompson 1988), an approach that originates in discourse analysis. In p-d terms an argument is good if it avoids committing a fallacy, whereas in RST terms an argument is good if it is coherent. RST has been criticised (Snoeck Henkemans 1997) for providing only a partially functional account of argument, and similar criticisms have been raised in the Natural Language Generation (NLG) community-particularly by Moore & Pollack (1992)- with regards to its account of intentionality in text in general. Mann and Thompson themselves note that although RST can be successfully applied to a wide range of texts from diverse domains, it fails to characterise some types of text, most notably legal contracts. There is ongoing research in the Artificial Intelligence and Law community exploring the potential for providing electronic support to contract negotiators, focusing on long-term, complex engineering agreements (see for example Daskalopulu & Sergot 1997). This paper provides a brief introduction to RST and illustrates its shortcomings with respect to contractual text. An alternative approach for modelling argument structure is presented which not only caters for contractual text, but also overcomes the aforementioned limitations of RST.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge