Modeling and Analysis of 2-Tier Heterogeneous Vehicular Networks Leveraging Roadside Units and Vehicle Relays
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2022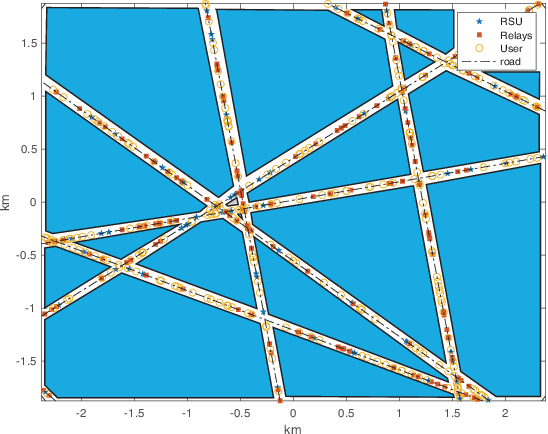
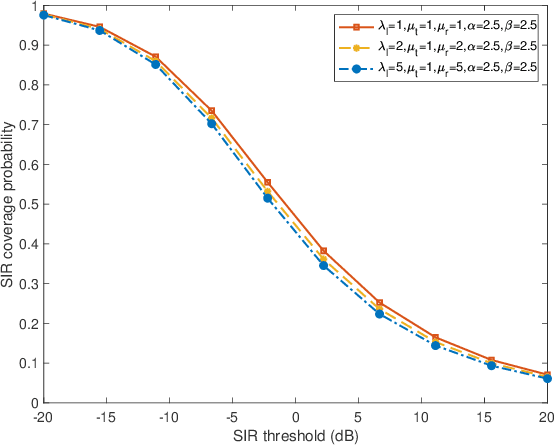
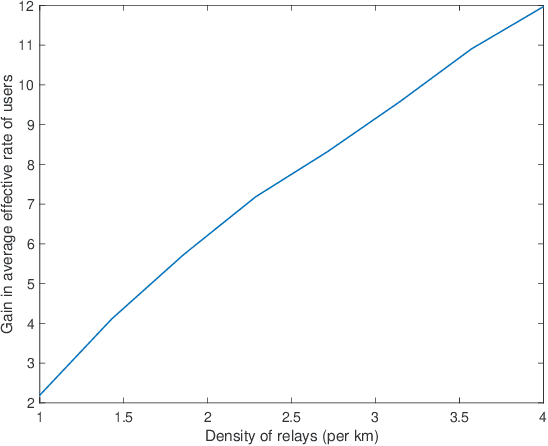
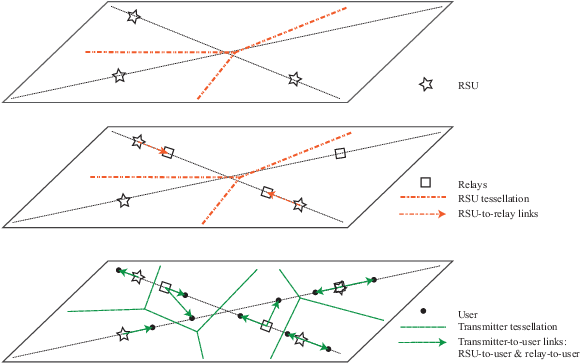
While roadside units (RSUs) play an essential role in vehicle-to-everything (V2X) by communicating with users, some users in congestion areas may not be well-served due to data traffic, signal attenuation, and interference. In these cases, vehicle relays can be employed to enhance the network topology to better serve those users. This paper leverages stochastic geometry to propose a novel framework for the performance analysis of heterogeneous vehicular networks with RSUs, vehicle relays, and vehicle users. We present a two-dimensional analytical model where the spatial dependence between RSUs, vehicle relays, vehicle users, and roads is accurately taken into account through a Cox point process structure. Assuming relays are backhauled to RSUs over a reserved wireless resource and users are associated with the closest RSU or relay, we derive the probability that the typical user is associated with either an RSU or a relay. Then, we derive the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) coverage probability of the typical user. Finally, using the derived formulas, we evaluate the average effective rate of the typical user in the network. This allows us to determine the gain of the average effective rate of users that results from the deployment of relays in the network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge