MLLMReID: Multimodal Large Language Model-based Person Re-identification
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2024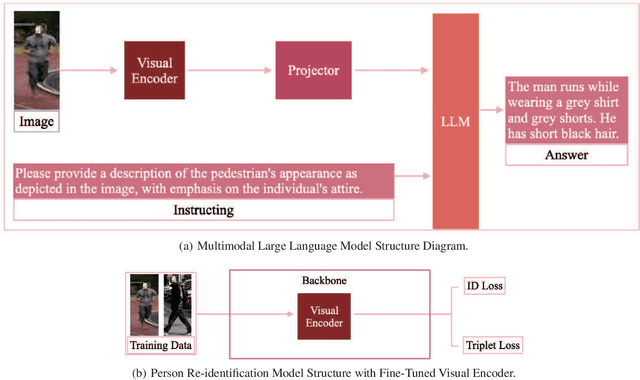
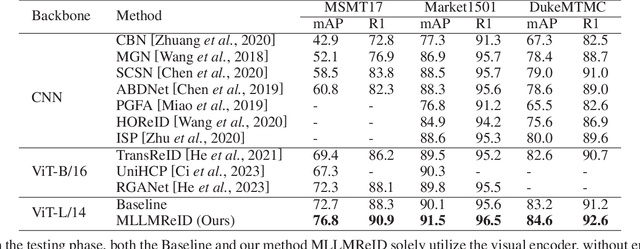
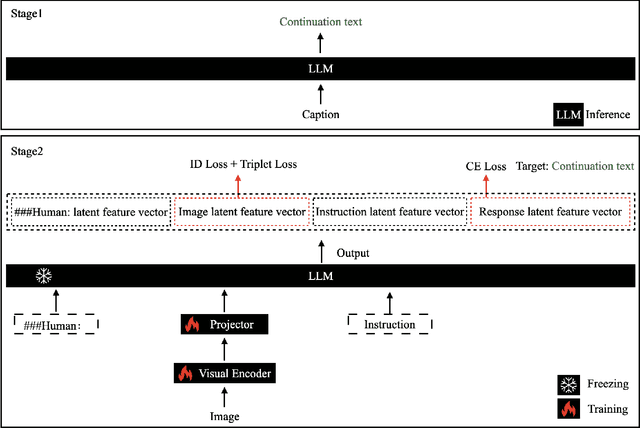
Multimodal large language models (MLLM) have achieved satisfactory results in many tasks. However, their performance in the task of person re-identification (ReID) has not been explored to date. This paper will investigate how to adapt them for the task of ReID. An intuitive idea is to fine-tune MLLM with ReID image-text datasets, and then use their visual encoder as a backbone for ReID. However, there still exist two apparent issues: (1) Designing instructions for ReID, MLLMs may overfit specific instructions, and designing a variety of instructions will lead to higher costs. (2) Latent image feature vectors from LLMs are not involved in loss computation. Instructional learning, aligning image-text features, results in indirect optimization and a learning objective that inadequately utilizes features, limiting effectiveness in person feature learning. To address these problems, this paper proposes MLLMReID: Multimodal Large Language Model-based ReID. Firstly, we proposed Common Instruction, a simple approach that leverages the essence ability of LLMs to continue writing, avoiding complex and diverse instruction design. Secondly, we proposed DirectReID, which effectively employs the latent image feature vectors of images outputted by LLMs in ReID tasks. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method. We will open-source the code on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge