ML-Assisted UE Positioning: Performance Analysis and 5G Architecture Enhancements
Paper and Code
Aug 25, 2021
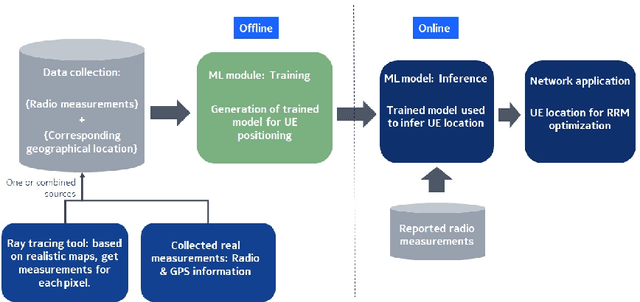
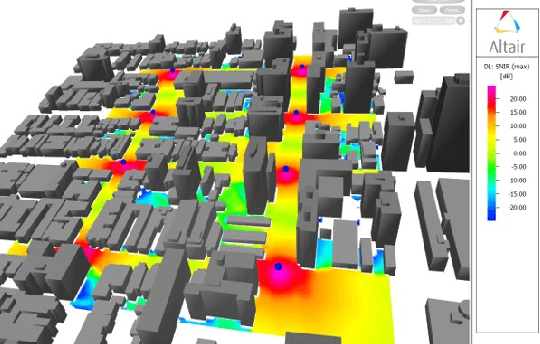
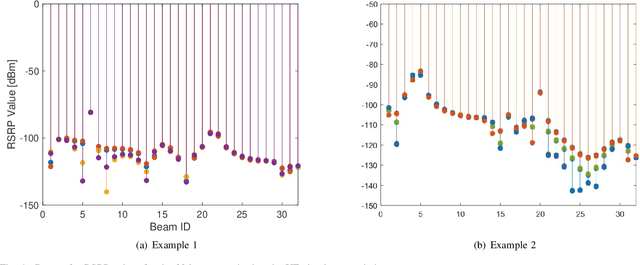
Artificial intelligence and data-driven networks will be integral part of 6G systems. In this article, we comprehensively discuss implementation challenges and need for architectural changes in 5G radio access networks for integrating machine learning (ML) solutions. As an example use case, we investigate user equipment (UE) positioning assisted by deep learning (DL) in 5G and beyond networks. As compared to state of the art positioning algorithms used in today's networks, radio signal fingerprinting and machine learning (ML) assisted positioning requires smaller additional feedback overhead; and the positioning estimates are made directly inside the radio access network (RAN), thereby assisting in radio resource management. In this regard, we study ML-assisted positioning methods and evaluate their performance using system level simulations for an outdoor scenario. The study is based on the use of raytracing tool, a 3GPP 5G NR compliant system level simulator and DL framework to estimate positioning accuracy of the UE. We evaluate and compare performance of various DL models and show mean positioning error in the range of 1-1.5m for a 2-hidden layer DL architecture with appropriate feature-modeling. Building on our performance analysis, we discuss pros and cons of various architectures to implement ML solutions for future networks and draw conclusions on the most suitable architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge