Mixed Dimension Embeddings with Application to Memory-Efficient Recommendation Systems
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2019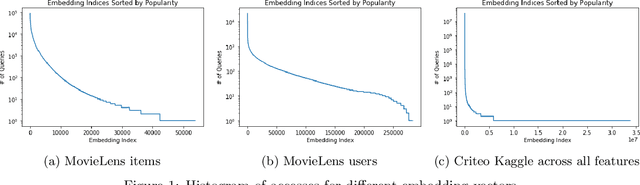

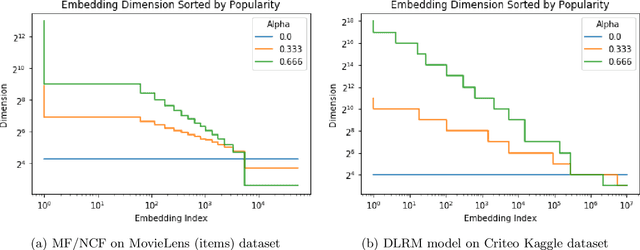
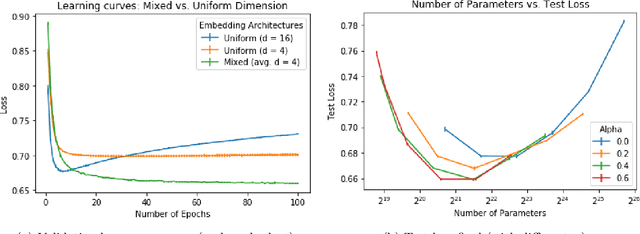
In many real-world applications, e.g. recommendation systems, certain items appear much more frequently than other items. However, standard embedding methods---which form the basis of many ML algorithms---allocate the same dimension to all of the items. This leads to statistical and memory inefficiencies. In this work, we propose mixed dimension embedding layers in which the dimension of a particular embedding vector can depend on the frequency of the item. This approach drastically reduces the memory requirement for the embedding, while maintaining and sometimes improving the ML performance. We show that the proposed mixed dimension layers achieve a higher accuracy, while using 8X fewer parameters, for collaborative filtering on the MovieLens dataset. Also, they improve accuracy by 0.1% using half as many parameters or maintain baseline accuracy using 16X fewer parameters for click-through rate prediction task on the Criteo Kaggle dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge