Metric learning approach for graph-based label propagation
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2016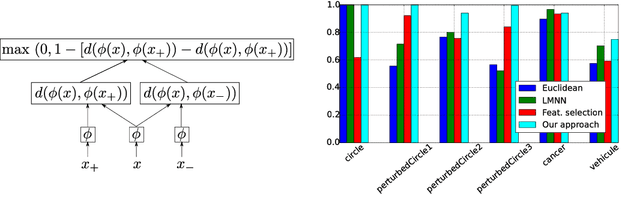
The efficiency of graph-based semi-supervised algorithms depends on the graph of instances on which they are applied. The instances are often in a vectorial form before a graph linking them is built. The construction of the graph relies on a metric over the vectorial space that help define the weight of the connection between entities. The classic choice for this metric is usually a distance measure or a similarity measure based on the euclidean norm. We claim that in some cases the euclidean norm on the initial vectorial space might not be the more appropriate to solve the task efficiently. We propose an algorithm that aims at learning the most appropriate vectorial representation for building a graph on which the task at hand is solved efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge