Memetic collaborative approaches for finding balanced incomplete block designs
Paper and Code
Nov 04, 2024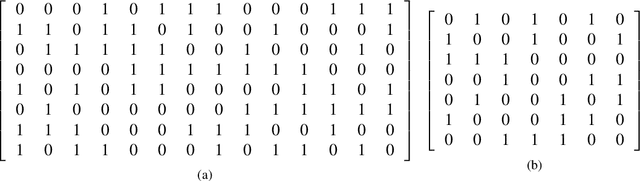
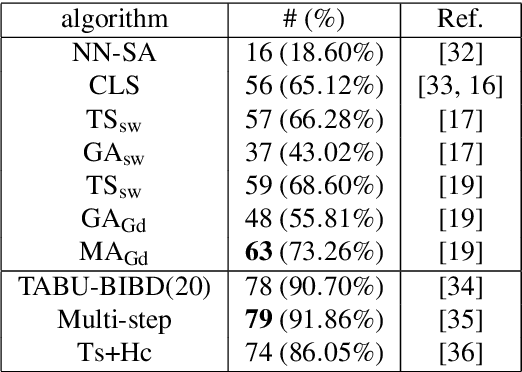
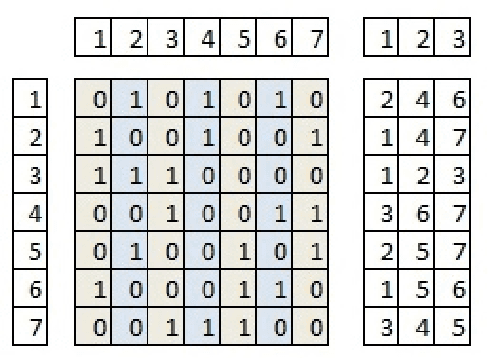
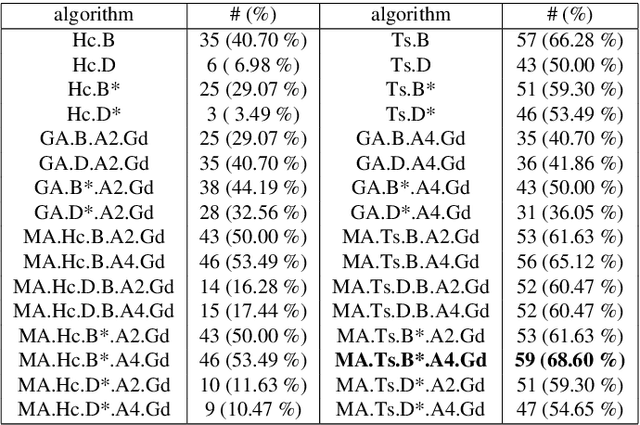
The balanced incomplete block design (BIBD) problem is a difficult combinatorial problem with a large number of symmetries, which add complexity to its resolution. In this paper, we propose a dual (integer) problem representation that serves as an alternative to the classical binary formulation of the problem. We attack this problem incrementally: firstly, we propose basic algorithms (i.e. local search techniques and genetic algorithms) intended to work separately on the two different search spaces (i.e. binary and integer); secondly, we propose two hybrid schemes: an integrative approach (i.e. a memetic algorithm) and a collaborative model in which the previous methods work in parallel, occasionally exchanging information. Three distinct two-dimensional structures are proposed as communication topology among the algorithms involved in the collaborative model, as well as a number of migration and acceptance criteria for sending and receiving data. An empirical analysis comparing a large number of instances of our schemes (with algorithms possibly working on different search spaces and with/without symmetry breaking methods) shows that some of these algorithms can be considered the state of the art of the metaheuristic methods applied to finding BIBDs. Moreover, our cooperative proposal is a general scheme from which distinct algorithmic variants can be instantiated to handle symmetrical optimisation problems. For this reason, we have also analysed its key parameters, thereby providing general guidelines for the design of efficient/robust cooperative algorithms devised from our proposal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge